第四章 Drupal源码分析
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
很多人,刚学Drupal的时候,常常会问这样的问题,Drupal是怎么生成这个页面的。比如,我们创建了第一个Drupal节点页面,“关于我们”,很多人,想知道这个页面是怎么组装起来的。想知道大致的流程。
问这个问题的人很多,所以每当我给人讲解Drupal模块开发的时候,首先带领学生分析的,就是这个节点页面的组装过程。有的人听着听着,就睡着了,而有的人则会听得津津有味。我们这里所讲的这些东西,就是这样,对你使用Drupal没有直接的帮助,但是能够帮助你更好的理解Drupal背后的机理,帮你建立学习Drupal的信心。
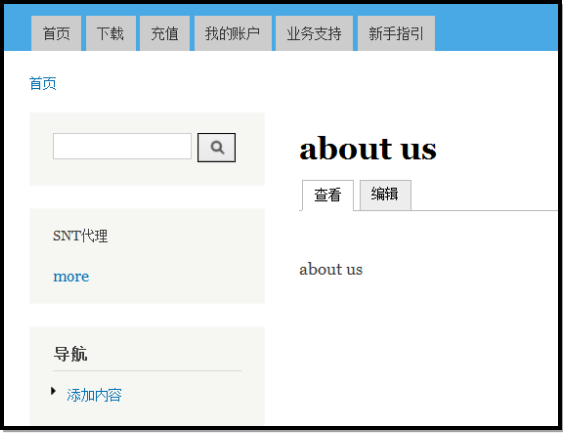
这就是我们创建的第一个节点页面,除了节点本身,还有导航链接,左边栏的区块,页脚的区块,这些东西共同的组成了一个页面。这个节点的路径为node/1,我们也可以使用别名aboutus。
Drupal版本:
10 完成阶段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们来看阶段7,也就是完成阶段,对应的代码:
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL:
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/common.inc';
_drupal_bootstrap_full();
break;
在这里,首先加载includes/common.inc文件,接着将这个阶段的工作,委托给了_drupal_bootstrap_full函数,注意这个函数位于common.inc文件中。我们打开这个文件,找到这个函数的定义:
function _drupal_bootstrap_full() {
static $called = FALSE;
if ($called) {
return;
}
$called = TRUE;
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/' . variable_get('path_inc', 'includes/path.inc');
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/theme.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/pager.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/' . variable_get('menu_inc', 'includes/menu.inc');
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/tablesort.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/file.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/unicode.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/image.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/form.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/mail.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/actions.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/ajax.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/token.inc';
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/errors.inc';
// Detect string handling method
unicode_check();
// Undo magic quotes
fix_gpc_magic();
// Load all enabled modules
module_load_all();
// Make sure all stream wrappers are registered.
file_get_stream_wrappers();
$test_info = &$GLOBALS['drupal_test_info'];
if (!empty($test_info['in_child_site'])) {
// Running inside the simpletest child site, log fatal errors to test
// specific file directory.
ini_set('log_errors', 1);
ini_set('error_log', 'public://error.log');
}
// Initialize $_GET['q'] prior to invoking hook_init().
drupal_path_initialize();
// Let all modules take action before the menu system handles the request.
// We do not want this while running update.php.
if (!defined('MAINTENANCE_MODE') || MAINTENANCE_MODE != 'update') {
// Prior to invoking hook_init(), initialize the theme (potentially a custom
// one for this page), so that:
// - Modules with hook_init() implementations that call theme() or
// theme_get_registry() don't initialize the incorrect theme.
// - The theme can have hook_*_alter() implementations affect page building
// (e.g., hook_form_alter(), hook_node_view_alter(), hook_page_alter()),
// ahead of when rendering starts.
menu_set_custom_theme();
drupal_theme_initialize();
module_invoke_all('init');
}
}
这个函数里面做的第一个工作,就是加载文件,path.inc、theme.inc、pager.inc、menu.inc、tablesort.inc、file.inc、unicode.inc、image.inc、form.inc、mail.inc、actions.inc、ajax.inc、token.inc、errors.inc就是在这个时候加载的。
unicode_check用来判断字符串处理方法,Drupal能够处理各种字符,这里需要检查一下PHP对unicode的支持。fix_gpc_magic,这个函数比较陌生,我后来查看函数的具体定义,和相关的文档,才弄明白的这个函数的作用,这个函数最终调用的是stripslashes,它的作用是去除转义反斜线,比如:
(\') 转换为(')。
双反斜线(\\)被转换为单个反斜线(\)。
module_load_all负责加载所有的module文件。file_get_stream_wrappers负责注册Drupal的流包装器(stream wrappers)。
$test_info这段代码,与simpletest有关,我们这里没有用到,所以跳过。
drupal_path_initialize负责路径的初始化,具体工作就是正确的设置$_GET['q']。
最后设置当前的主题,初始化主题,触发hook_init钩子。到此,整个引导指令就全部完成了,Drupal已经启动起来了。
Drupal版本:
11 页面内容的生成与组装
Drupal启动以后,接下来做什么?我们回到index.php文件,接下来执行的是menu_execute_active_handler函数,就执行了这么一个函数,就完了。我们现在要做的是分析这个函数,看看在这个函数里面,Drupal具体做了什么。这个函数以menu开头,所以我推测它位于includes里面menu.inc文件中。我们也可以使用Google,搜索一下这个函数,这样会印证我前面的猜测。其实第一次的时候,我也不知道,也是Google出来的。
Drupal版本:
12 菜单回调机制
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
打开menu.inc文件,找到menu_execute_active_handler函数,阅读这个函数的源代码。
/**
* Execute the page callback associated with the current path.
*
* @param $path
* The drupal path whose handler is to be be executed. If set to NULL, then
* the current path is used.
* @param $deliver
* (optional) A boolean to indicate whether the content should be sent to the
* browser using the appropriate delivery callback (TRUE) or whether to return
* the result to the caller (FALSE).
*/
function menu_execute_active_handler($path = NULL, $deliver = TRUE) {
// Check if site is offline.
$page_callback_result = _menu_site_is_offline() ? MENU_SITE_OFFLINE : MENU_SITE_ONLINE;
// Allow other modules to change the site status but not the path because that
// would not change the global variable. hook_url_inbound_alter() can be used
// to change the path. Code later will not use the $read_only_path variable.
$read_only_path = !empty($path) ? $path : $_GET['q'];
drupal_alter('menu_site_status', $page_callback_result, $read_only_path);
// Only continue if the site status is not set.
if ($page_callback_result == MENU_SITE_ONLINE) {
if ($router_item = menu_get_item($path)) {
if ($router_item['access']) {
if ($router_item['include_file']) {
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/' . $router_item['include_file'];
}
$page_callback_result = call_user_func_array($router_item['page_callback'], $router_item['page_arguments']);
}
else {
$page_callback_result = MENU_ACCESS_DENIED;
}
}
else {
$page_callback_result = MENU_NOT_FOUND;
}
}
// Deliver the result of the page callback to the browser, or if requested,
// return it raw, so calling code can do more processing.
if ($deliver) {
$default_delivery_callback = (isset($router_item) && $router_item) ? $router_item['delivery_callback'] : NULL;
drupal_deliver_page($page_callback_result, $default_delivery_callback);
}
else {
return $page_callback_result;
}
}
这个函数,执行当前路径的对应页面回调,向浏览器返回具体的页面。这个函数包含两个参数$path和$deliver,不过这两个参数都是可选的;在index.php里面调用这个函数的时候,也没有传递参数,所以这两个参数现在是默认值。
第一行代码,是检查当前站点是否是在线状态。Drupal支持离线状态,什么时候用到离线状态,网站升级的时候,通常把站点配置为离线状态。离线配置地址位于admin/config/development/maintenance。

我们这里访问的node/1,当前状态为在线状态。_menu_site_is_offline是一个帮助函数,用来检查站点是否离线。
接下来的代码:
drupal_alter('menu_site_status', $page_callback_result, $read_only_path)
用来允许其它模块修改站点状态,这里面只允许修改站点状态,不允许修改当前路径。如果要修改路径的话,可以使用hook_url_inbound_alter。
再往下是if语句,我们的站点当前为在线,所以进入了if语句里面,里面还是一个if语句:
if ($router_item = menu_get_item($path)) {
在我们这里,$path的值为NULL,menu_get_item会获取当前路径对应的菜单项。当前路径为node/1,对应的菜单项node/%,这个是在node_menu里面定义的,我们打开node.module文件,找到node_menu,找到node/%对应的菜单项。对应的定义如下:
$items['node/%node'] = array(
'title callback' => 'node_page_title',
'title arguments' => array(1),
// The page callback also invokes drupal_set_title() in case
// the menu router's title is overridden by a menu link.
'page callback' => 'node_page_view',
'page arguments' => array(1),
'access callback' => 'node_access',
'access arguments' => array('view', 1),
);
menu_get_item里面返回的信息,和hook_menu里面定义的菜单项,存在着一一对应的关系,当然menu_get_item里面包含更多一些属性。
此时,$router_item不为空,所以我们继续往下执行。接下来检查路由项的访问权限,看当前用户是否有权限访问这个页面。
if ($router_item['access'])
我们这里是有权限的,所以继续执行里面的代码:
if ($router_item['include_file']) {
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/' . $router_item['include_file'];
}
$page_callback_result = call_user_func_array($router_item['page_callback'], $router_item['page_arguments']);
$router_item['include_file']指的是什么?我们看node_menu,找到下面的代码:
$items['node/%node/edit'] = array(
'title' => 'Edit',
'page callback' => 'node_page_edit',
'page arguments' => array(1),
'access callback' => 'node_access',
'access arguments' => array('update', 1),
'weight' => 0,
'type' => MENU_LOCAL_TASK,
'context' => MENU_CONTEXT_PAGE | MENU_CONTEXT_INLINE,
'file' => 'node.pages.inc',
);
$items['node/%node/delete'] = array(
'title' => 'Delete',
'page callback' => 'drupal_get_form',
'page arguments' => array('node_delete_confirm', 1),
'access callback' => 'node_access',
'access arguments' => array('delete', 1),
'weight' => 1,
'type' => MENU_LOCAL_TASK,
'context' => MENU_CONTEXT_INLINE,
'file' => 'node.pages.inc',
);
这里的’file’键,就对应于$router_item['include_file'],如果路由里面指定了这个文件,Drupal在执行回调函数之前,会尝试加载这个文件。比如我们访问node/1/edit,对应的菜单项为'node/%node/edit',在菜单项的定义里面,存在'file' => 'node.pages.inc',当程序执行到这里的时候,Drupal就会尝试加载文件node.pages.inc。
这样做有什么好处?好处,就是将页面回调函数的逻辑代码,从module文件中分离出来,使得module文件尽可能的小。Drupal是很吃内存的,其中的一个重要的原因,就是Drupal启动后,会加载所有的module文件,如果每个module文件都比较小的话,那么消耗的内存就比较小。我们在think in Drupal的第一集里面,介绍过这个问题,我们今天通过阅读Drupal核心的源代码,进一步了解到,核心的具体实现办法。
Drupal版本:
13 主内容的生成
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
下面来看这句抽象的代码:
$page_callback_result = call_user_func_array($router_item['page_callback'], $router_item['page_arguments']);
首先我们需要知道,$router_item['page_callback']和$router_item['page_arguments']的值在当前情况下是什么。现在的路径为node/1。它对应的:
$router_item['page_callback'] : node_page_view
$router_item['page_arguments'] : array(1)
注意,这里的array(1),表示arg(1),Drupal向node_page_view传递参数的时候,会做以下工作:
$nid = arg(1);
$node = node_load($nid);
对于node/1/edit,arg(0)就是node,arg(1)就是1,arg(2)就是edit,依次类推。这个参数的传递过程,是Drupal菜单系统的一种特有机制,我们了解就可以了,知道这里传递过来的是$node对象。
我们把前面抽象的函数,换成具体的情况:
$page_callback_result = call_user_func_array(‘node_page_view’, array($node));
call_user_func_array是一个PHP函数,我刚开始看到这个函数的时候,感到头大。查了一下文档,明白了它是用来动态的调用函数的。上面的这行代码,就等价于:
call_user_func_array(‘node_page_view’, array($node)) = node_page_view($node);
实际上,就是这样的:
$page_callback_result = node_page_view($node);
这是当路径为node/1时的情况。当路径为node/1/edit的时候,执行到这里,实际情况是这样的:
$page_callback_result = node_page_edit($node);
这里具体执行的这个回调函数,是动态的,路径不一样,对应的回调函数也不一样。
Drupal版本:
14 node_page_view代码追踪
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
现在让我们来看一下node_page_view返回了什么,我们在node.module里面找到这个函数。
/**
* Menu callback: Displays a single node.
*
* @param $node
* The node object.
*
* @return
* A page array suitable for use by drupal_render().
*
* @see node_menu()
*/
function node_page_view($node) {
// If there is a menu link to this node, the link becomes the last part
// of the active trail, and the link name becomes the page title.
// Thus, we must explicitly set the page title to be the node title.
drupal_set_title($node->title);
$uri = entity_uri('node', $node);
// Set the node path as the canonical URL to prevent duplicate content.
drupal_add_html_head_link(array('rel' => 'canonical', 'href' => url($uri['path'], $uri['options'])), TRUE);
// Set the non-aliased path as a default shortlink.
drupal_add_html_head_link(array('rel' => 'shortlink', 'href' => url($uri['path'], array_merge($uri['options'], array('alias' => TRUE)))), TRUE);
return node_show($node);
}
这里面具体复杂的是node_show($node),我们来看node_show的定义:
/**
* Generates an array which displays a node detail page.
*
* @param $node
* A node object.
* @param $message
* A flag which sets a page title relevant to the revision being viewed.
*
* @return
* A $page element suitable for use by drupal_render().
*/
function node_show($node, $message = FALSE) {
if ($message) {
drupal_set_title(t('Revision of %title from %date', array('%title' => $node->title, '%date' => format_date($node->revision_timestamp))), PASS_THROUGH);
}
// For markup consistency with other pages, use node_view_multiple() rather than node_view().
$nodes = node_view_multiple(array($node->nid => $node), 'full');
// Update the history table, stating that this user viewed this node.
node_tag_new($node);
return $nodes;
}
这里返回的是一个数组,Drupal将具体的实现又交给了node_view_multiple,只不过当前只有一个节点。我们来看node_view_multiple:
/**
* Constructs a drupal_render() style array from an array of loaded nodes.
*
* @param $nodes
* An array of nodes as returned by node_load_multiple().
* @param $view_mode
* View mode, e.g. 'full', 'teaser'...
* @param $weight
* An integer representing the weight of the first node in the list.
* @param $langcode
* (optional) A language code to use for rendering. Defaults to NULL which is
* the global content language of the current request.
*
* @return
* An array in the format expected by drupal_render().
*/
function node_view_multiple($nodes, $view_mode = 'teaser', $weight = 0, $langcode = NULL) {
field_attach_prepare_view('node', $nodes, $view_mode, $langcode);
entity_prepare_view('node', $nodes, $langcode);
$build = array();
foreach ($nodes as $node) {
$build['nodes'][$node->nid] = node_view($node, $view_mode, $langcode);
$build['nodes'][$node->nid]['#weight'] = $weight;
$weight++;
}
$build['nodes']['#sorted'] = TRUE;
return $build;
}
这里返回的是一个数组,包含节点的数组,可以使用drupal_render呈现这个数组。而这里,单个节点的构件,则是由node_view完成的。
/**
* Generates an array for rendering the given node.
*
* @param $node
* A node object.
* @param $view_mode
* View mode, e.g. 'full', 'teaser'...
* @param $langcode
* (optional) A language code to use for rendering. Defaults to the global
* content language of the current request.
*
* @return
* An array as expected by drupal_render().
*/
function node_view($node, $view_mode = 'full', $langcode = NULL) {
if (!isset($langcode)) {
$langcode = $GLOBALS['language_content']->language;
}
// Populate $node->content with a render() array.
node_build_content($node, $view_mode, $langcode);
$build = $node->content;
// We don't need duplicate rendering info in node->content.
unset($node->content);
$build += array(
'#theme' => 'node',
'#node' => $node,
'#view_mode' => $view_mode,
'#language' => $langcode,
);
// Add contextual links for this node, except when the node is already being
// displayed on its own page. Modules may alter this behavior (for example,
// to restrict contextual links to certain view modes) by implementing
// hook_node_view_alter().
if (!empty($node->nid) && !($view_mode == 'full' && node_is_page($node))) {
$build['#contextual_links']['node'] = array('node', array($node->nid));
}
// Allow modules to modify the structured node.
$type = 'node';
drupal_alter(array('node_view', 'entity_view'), $build, $type);
return $build;
}
这里我们可以看一下,这个数组的具体结构,如粗体代码所示。node_build_content,这个我们就不往下追踪了,有兴趣的可以继续往下分析下去。
Drupal版本:
15 SQL语句的调用
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
曾经有人在这里,问过我一个这样的问题,我怎么没有看到SQL语句啊?我们前面讲了,在向node_page_view传递参数之前,调用了node_load函数,将节点ID转为了节点对象。我们来看一下node_load函数的定义。
/**
* Loads a node object from the database.
*
* @param $nid
* The node ID.
* @param $vid
* The revision ID.
* @param $reset
* Whether to reset the node_load_multiple cache.
*
* @return
* A fully-populated node object, or FALSE if the node is not found.
*/
function node_load($nid = NULL, $vid = NULL, $reset = FALSE) {
$nids = (isset($nid) ? array($nid) : array());
$conditions = (isset($vid) ? array('vid' => $vid) : array());
$node = node_load_multiple($nids, $conditions, $reset);
return $node ? reset($node) : FALSE;
}
它将单个节点的加载委托给了node_load_multiple,只不过这里传递过来一个节点ID而已。我们往下看node_load_multiple。
/**
* Loads node entities from the database.
*
* This function should be used whenever you need to load more than one node
* from the database. Nodes are loaded into memory and will not require database
* access if loaded again during the same page request.
*
* @see entity_load()
* @see EntityFieldQuery
*
* @param $nids
* An array of node IDs.
* @param $conditions
* (deprecated) An associative array of conditions on the {node}
* table, where the keys are the database fields and the values are the
* values those fields must have. Instead, it is preferable to use
* EntityFieldQuery to retrieve a list of entity IDs loadable by
* this function.
* @param $reset
* Whether to reset the internal node_load cache.
*
* @return
* An array of node objects indexed by nid.
*
* @todo Remove $conditions in Drupal 8.
*/
function node_load_multiple($nids = array(), $conditions = array(), $reset = FALSE) {
return entity_load('node', $nids, $conditions, $reset);
}
node_load_multiple又将具体的实现,委托给了entity_load。我们通过Google搜索一下entity_load,发现这个函数位于includes/common.inc里面,这让人有点意外。Fago对这一点就提出了批评,说entity的函数放的哪都是,Drupal8在这方面做了改进,Fago的有关实体的想法进入了内核。
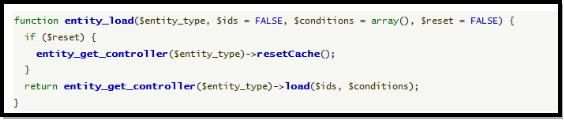
不过这里面仍然没有SQL语句。我们在这个api.drupal.org上,在代码的上面,有这么一部分:

我们点击DrupalDefaultEntityController,进入页面https://api.drupal.org/api/drupal/includes%21entity.inc/class/DrupalDefaultEntityController/7,找到:
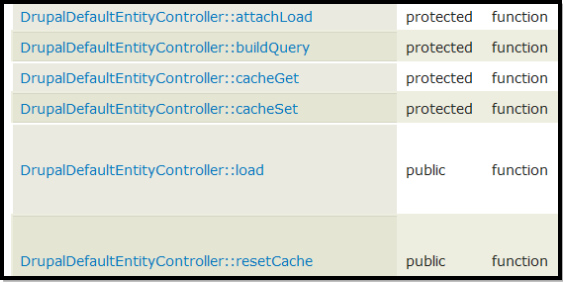
点击这里的DrupalDefaultEntityController::load。阅读这个成员函数,在代码里面找到:
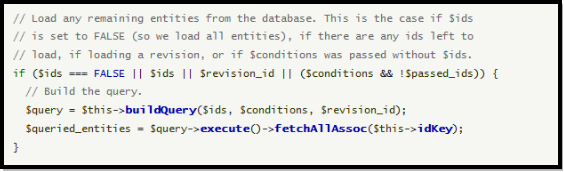
我们看到SQL语句的构建,是由DrupalDefaultEntityController::buildQuery完成的,我们点击这个成员函数,查看对应的源代码,这里面,我们看到了SQL语句:
protected function buildQuery($ids, $conditions = array(), $revision_id = FALSE) {
$query = db_select($this->entityInfo['base table'], 'base');
$query->addTag($this->entityType . '_load_multiple');
if ($revision_id) {
$query->join($this->revisionTable, 'revision', "revision.{$this->idKey} = base.{$this->idKey} AND revision.{$this->revisionKey} = :revisionId", array(':revisionId' => $revision_id));
}
elseif ($this->revisionKey) {
$query->join($this->revisionTable, 'revision', "revision.{$this->revisionKey} = base.{$this->revisionKey}");
}
// Add fields from the {entity} table.
$entity_fields = $this->entityInfo['schema_fields_sql']['base table'];
if ($this->revisionKey) {
// Add all fields from the {entity_revision} table.
$entity_revision_fields = drupal_map_assoc($this->entityInfo['schema_fields_sql']['revision table']);
// The id field is provided by entity, so remove it.
unset($entity_revision_fields[$this->idKey]);
// Remove all fields from the base table that are also fields by the same
// name in the revision table.
$entity_field_keys = array_flip($entity_fields);
foreach ($entity_revision_fields as $key => $name) {
if (isset($entity_field_keys[$name])) {
unset($entity_fields[$entity_field_keys[$name]]);
}
}
$query->fields('revision', $entity_revision_fields);
}
$query->fields('base', $entity_fields);
if ($ids) {
$query->condition("base.{$this->idKey}", $ids, 'IN');
}
if ($conditions) {
foreach ($conditions as $field => $value) {
$query->condition('base.' . $field, $value);
}
}
return $query;
}
这段代码仍然很抽象,从这里面,我们可以看出,Drupal在PHP的基础之上,为我们封装了很多层。
Drupal版本:
16 页面内容组装
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
现在,包含节点对象的可呈现数组,已经返回来了。这个页面是怎么构件出来的呢?让我们回到函数menu_execute_active_handler上面来。
$page_callback_result = MENU_ACCESS_DENIED;
$page_callback_result = MENU_NOT_FOUND;
这两种特殊情况我们就不分析了。往下看。
if ($deliver) {
$default_delivery_callback = (isset($router_item) && $router_item) ? $router_item['delivery_callback'] : NULL;
drupal_deliver_page($page_callback_result, $default_delivery_callback);
}
else {
return $page_callback_result;
}
我们没有向menu_execute_active_handler传递参数,所以这里的$deliver为TRUE,将会执行if语句里面的代码。
Drupal版本:
16.1 drupal_deliver_html_page
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们在node_menu里面,并没有定义'delivery callback',所以这里的$default_delivery_callback将会使用Drupal的默认值。$page_callback_result就是刚才返回的包含节点对象的呈现数组。现在,让我们来看一下drupal_deliver_page,是怎么将这个数组转换成整个页面,并返回给浏览器的。
function drupal_deliver_page($page_callback_result, $default_delivery_callback = NULL) {
if (!isset($default_delivery_callback) && ($router_item = menu_get_item())) {
$default_delivery_callback = $router_item['delivery_callback'];
}
$delivery_callback = !empty($default_delivery_callback) ? $default_delivery_callback : 'drupal_deliver_html_page';
// Give modules a chance to alter the delivery callback used, based on
// request-time context (e.g., HTTP request headers).
drupal_alter('page_delivery_callback', $delivery_callback);
if (function_exists($delivery_callback)) {
$delivery_callback($page_callback_result);
}
else {
// If a delivery callback is specified, but doesn't exist as a function,
// something is wrong, but don't print anything, since it's not known
// what format the response needs to be in.
watchdog('delivery callback not found', 'callback %callback not found: %q.', array('%callback' => $delivery_callback, '%q' => $_GET['q']), WATCHDOG_ERROR);
}
}
实际上我们并没有在任何地方设置$delivery_callback,所以将会使用默认的'drupal_deliver_html_page'。这里的
drupal_alter('page_delivery_callback', $delivery_callback);
用来允许第三方模块修改这里的$delivery_callback,但是实际上,我基本上没有见过哪个第三方模块实现了这个钩子函数。Drupal提供了太多的钩子函数,有些可能从来没有被使用过。
function_exists负责检查函数是否存在,drupal_deliver_html_page这个函数是存在的,所以这里实际调用的是:
drupal_deliver_html_page($page_callback_result);
为什么不直接调用drupal_deliver_html_page呢?我们要的就是html页面啊。Drupal核心的开发者是这样考虑的,这个地方留个接口,这样第三方模块就可以实现,比如说:
drupal_deliver_json_page
drupal_deliver_xml_page
也就是说,Drupal不仅仅支持HTML,返回有可能还是json、xml等其它格式。我们这里只用到了html,所以让我们来看一下默认的具体实现。
/**
* Packages and sends the result of a page callback to the browser as HTML.
*
* @param $page_callback_result
* The result of a page callback. Can be one of:
* - NULL: to indicate no content.
* - An integer menu status constant: to indicate an error condition.
* - A string of HTML content.
* - A renderable array of content.
*
* @see drupal_deliver_page()
*/
function drupal_deliver_html_page($page_callback_result) {
// Emit the correct charset HTTP header, but not if the page callback
// result is NULL, since that likely indicates that it printed something
// in which case, no further headers may be sent, and not if code running
// for this page request has already set the content type header.
if (isset($page_callback_result) && is_null(drupal_get_http_header('Content-Type'))) {
drupal_add_http_header('Content-Type', 'text/html; charset=utf-8');
}
// Send appropriate HTTP-Header for browsers and search engines.
global $language;
drupal_add_http_header('Content-Language', $language->language);
// Menu status constants are integers; page content is a string or array.
if (is_int($page_callback_result)) {
// @todo: Break these up into separate functions?
switch ($page_callback_result) {
case MENU_NOT_FOUND:
// Print a 404 page.
drupal_add_http_header('Status', '404 Not Found');
watchdog('page not found', check_plain($_GET['q']), NULL, WATCHDOG_WARNING);
// Check for and return a fast 404 page if configured.
drupal_fast_404();
// Keep old path for reference, and to allow forms to redirect to it.
if (!isset($_GET['destination'])) {
$_GET['destination'] = $_GET['q'];
}
$path = drupal_get_normal_path(variable_get('site_404', ''));
if ($path && $path != $_GET['q']) {
// Custom 404 handler. Set the active item in case there are tabs to
// display, or other dependencies on the path.
menu_set_active_item($path);
$return = menu_execute_active_handler($path, FALSE);
}
if (empty($return) || $return == MENU_NOT_FOUND || $return == MENU_ACCESS_DENIED) {
// Standard 404 handler.
drupal_set_title(t('Page not found'));
$return = t('The requested page "@path" could not be found.', array('@path' => request_uri()));
}
drupal_set_page_content($return);
$page = element_info('page');
print drupal_render_page($page);
break;
case MENU_ACCESS_DENIED:
// Print a 403 page.
drupal_add_http_header('Status', '403 Forbidden');
watchdog('access denied', check_plain($_GET['q']), NULL, WATCHDOG_WARNING);
// Keep old path for reference, and to allow forms to redirect to it.
if (!isset($_GET['destination'])) {
$_GET['destination'] = $_GET['q'];
}
$path = drupal_get_normal_path(variable_get('site_403', ''));
if ($path && $path != $_GET['q']) {
// Custom 403 handler. Set the active item in case there are tabs to
// display or other dependencies on the path.
menu_set_active_item($path);
$return = menu_execute_active_handler($path, FALSE);
}
if (empty($return) || $return == MENU_NOT_FOUND || $return == MENU_ACCESS_DENIED) {
// Standard 403 handler.
drupal_set_title(t('Access denied'));
$return = t('You are not authorized to access this page.');
}
print drupal_render_page($return);
break;
case MENU_SITE_OFFLINE:
// Print a 503 page.
drupal_maintenance_theme();
drupal_add_http_header('Status', '503 Service unavailable');
drupal_set_title(t('Site under maintenance'));
print theme('maintenance_page', array('content' => filter_xss_admin(variable_get('maintenance_mode_message',
t('@site is currently under maintenance. We should be back shortly. Thank you for your patience.', array('@site' => variable_get('site_name', 'Drupal')))))));
break;
}
}
elseif (isset($page_callback_result)) {
// Print anything besides a menu constant, assuming it's not NULL or
// undefined.
print drupal_render_page($page_callback_result);
}
// Perform end-of-request tasks.
drupal_page_footer();
}
最前面的两端代码,是用来添加http header的(drupal_add_http_header),我们不用去管它。
再往下是对$page_callback_result做了整数判断。
if (is_int($page_callback_result)) {
什么时候会是整数呢,当MENU_NOT_FOUND、MENU_ACCESS_DENIED、MENU_SITE_OFFLINE的时候,会是整数。我们这里面返回的是数组,不是整数,我们这里也就跳过了这三种特殊情况,继续往下看代码。
elseif (isset($page_callback_result)) {
// Print anything besides a menu constant, assuming it's not NULL or
// undefined.
print drupal_render_page($page_callback_result);
}
// Perform end-of-request tasks.
drupal_page_footer();
Drupal版本:
16.2 页面数组的合成
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
这是我们这里实际执行的语句。用来合成页面的是drupal_render_page函数。这个时候,传递过来的$page_callback_result,只是一个包含节点对象的呈现数组,节点外面的区域、区块是怎么加进来的呢?这是很多初学者的疑问。让我们来看这个函数的定义:
/**
* Renders the page, including all theming.
*
* @param $page
* A string or array representing the content of a page. The array consists of
* the following keys:
* - #type: Value is always 'page'. This pushes the theming through
* page.tpl.php (required).
* - #show_messages: Suppress drupal_get_message() items. Used by Batch
* API (optional).
*
* @see hook_page_alter()
* @see element_info()
*/
function drupal_render_page($page) {
$main_content_display = &drupal_static('system_main_content_added', FALSE);
// Allow menu callbacks to return strings or arbitrary arrays to render.
// If the array returned is not of #type page directly, we need to fill
// in the page with defaults.
if (is_string($page) || (is_array($page) && (!isset($page['#type']) || ($page['#type'] != 'page')))) {
drupal_set_page_content($page);
$page = element_info('page');
}
// Modules can add elements to $page as needed in hook_page_build().
foreach (module_implements('page_build') as $module) {
$function = $module . '_page_build';
$function($page);
}
// Modules alter the $page as needed. Blocks are populated into regions like
// 'sidebar_first', 'footer', etc.
drupal_alter('page', $page);
// If no module has taken care of the main content, add it to the page now.
// This allows the site to still be usable even if no modules that
// control page regions (for example, the Block module) are enabled.
if (!$main_content_display) {
$page['content']['system_main'] = drupal_set_page_content();
}
return drupal_render($page);
}
这个时候会组装$page这个数组,开始的时候,只包含节点部分,注意往下执行的时候,粗体部分的代码,定义了hook_page_build钩子函数,允许其它模块向$page数组追加内容。难道block模块实现了这个钩子函数?
Drupal版本:
16.3 通过hook_page_build组装区域区块
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
让我们来试一下,打开block.module文件,搜索block_page_build,还真找到了。真聪明,你猜对了。我们来看一下block模块的具体实现。
/**
* Implements hook_page_build().
*
* Renders blocks into their regions.
*/
function block_page_build(&$page) {
global $theme;
// The theme system might not yet be initialized. We need $theme.
drupal_theme_initialize();
// Fetch a list of regions for the current theme.
$all_regions = system_region_list($theme);
$item = menu_get_item();
if ($item['path'] != 'admin/structure/block/demo/' . $theme) {
// Load all region content assigned via blocks.
foreach (array_keys($all_regions) as $region) {
// Assign blocks to region.
if ($blocks = block_get_blocks_by_region($region)) {
$page[$region] = $blocks;
}
}
// Once we've finished attaching all blocks to the page, clear the static
// cache to allow modules to alter the block list differently in different
// contexts. For example, any code that triggers hook_page_build() more
// than once in the same page request may need to alter the block list
// differently each time, so that only certain parts of the page are
// actually built. We do not clear the cache any earlier than this, though,
// because it is used each time block_get_blocks_by_region() gets called
// above.
drupal_static_reset('block_list');
}
else {
// Append region description if we are rendering the regions demo page.
$item = menu_get_item();
if ($item['path'] == 'admin/structure/block/demo/' . $theme) {
$visible_regions = array_keys(system_region_list($theme, REGIONS_VISIBLE));
foreach ($visible_regions as $region) {
$description = '<div class="block-region">' . $all_regions[$region] . '</div>';
$page[$region]['block_description'] = array(
'#markup' => $description,
'#weight' => 15,
);
}
$page['page_top']['backlink'] = array(
'#type' => 'link',
'#title' => t('Exit block region demonstration'),
'#href' => 'admin/structure/block' . (variable_get('theme_default', 'bartik') == $theme ? '' : '/list/' . $theme),
// Add the "overlay-restore" class to indicate this link should restore
// the context in which the region demonstration page was opened.
'#options' => array('attributes' => array('class' => array('block-demo-backlink', 'overlay-restore'))),
'#weight' => -10,
);
}
}
}
Block模块,在这里会找到当前主题的所有的区域,对于每个区域,会加载这个区域里面的所有的当前可用的区块。以区域的机读名字为键,把区域里面的内容追加到$page数组上来。
代码里面的:
if ($item['path'] == 'admin/structure/block/demo/' . $theme) {
这是一种非常特殊的情况,只有在区块的管理界面,显示一个主题的演示区域的时候,才会用到,所以里面的代码,我们这里不用深究。
Drupal版本:
16.4 使用drupal_render呈现页面数组
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
现在,整个$page数组已经构建完成了,Drupal是怎么把它转为HTML页面的呢?注意这里的这个数组的类型是page,这个和表单元素数组,是一样的。Drupal6里面的表单数组,在Drupal7下,概念上做了进一步的扩充,除了表单元素以外,区块、节点、页面都是以呈现数组的形式出现。所有的呈现数组,经过drupal_render函数处理,就会转换成对应HTML形式。我们来看一下drupal_render的定义。
function drupal_render(&$elements) {
// Early-return nothing if user does not have access.
if (empty($elements) || (isset($elements['#access']) && !$elements['#access'])) {
return;
}
// Do not print elements twice.
if (!empty($elements['#printed'])) {
return;
}
// Try to fetch the element's markup from cache and return.
if (isset($elements['#cache'])) {
$cached_output = drupal_render_cache_get($elements);
if ($cached_output !== FALSE) {
return $cached_output;
}
}
// If #markup is set, ensure #type is set. This allows to specify just #markup
// on an element without setting #type.
if (isset($elements['#markup']) && !isset($elements['#type'])) {
$elements['#type'] = 'markup';
}
// If the default values for this element have not been loaded yet, populate
// them.
if (isset($elements['#type']) && empty($elements['#defaults_loaded'])) {
$elements += element_info($elements['#type']);
}
// Make any final changes to the element before it is rendered. This means
// that the $element or the children can be altered or corrected before the
// element is rendered into the final text.
if (isset($elements['#pre_render'])) {
foreach ($elements['#pre_render'] as $function) {
if (function_exists($function)) {
$elements = $function($elements);
}
}
}
// Allow #pre_render to abort rendering.
if (!empty($elements['#printed'])) {
return;
}
// Get the children of the element, sorted by weight.
$children = element_children($elements, TRUE);
// Initialize this element's #children, unless a #pre_render callback already
// preset #children.
if (!isset($elements['#children'])) {
$elements['#children'] = '';
}
// Call the element's #theme function if it is set. Then any children of the
// element have to be rendered there.
if (isset($elements['#theme'])) {
$elements['#children'] = theme($elements['#theme'], $elements);
}
// If #theme was not set and the element has children, render them now.
// This is the same process as drupal_render_children() but is inlined
// for speed.
if ($elements['#children'] == '') {
foreach ($children as $key) {
$elements['#children'] .= drupal_render($elements[$key]);
}
}
// Let the theme functions in #theme_wrappers add markup around the rendered
// children.
if (isset($elements['#theme_wrappers'])) {
foreach ($elements['#theme_wrappers'] as $theme_wrapper) {
$elements['#children'] = theme($theme_wrapper, $elements);
}
}
// Filter the outputted content and make any last changes before the
// content is sent to the browser. The changes are made on $content
// which allows the output'ed text to be filtered.
if (isset($elements['#post_render'])) {
foreach ($elements['#post_render'] as $function) {
if (function_exists($function)) {
$elements['#children'] = $function($elements['#children'], $elements);
}
}
}
// Add any JavaScript state information associated with the element.
if (!empty($elements['#states'])) {
drupal_process_states($elements);
}
// Add additional libraries, CSS, JavaScript an other custom
// attached data associated with this element.
if (!empty($elements['#attached'])) {
drupal_process_attached($elements);
}
$prefix = isset($elements['#prefix']) ? $elements['#prefix'] : '';
$suffix = isset($elements['#suffix']) ? $elements['#suffix'] : '';
$output = $prefix . $elements['#children'] . $suffix;
// Cache the processed element if #cache is set.
if (isset($elements['#cache'])) {
drupal_render_cache_set($output, $elements);
}
$elements['#printed'] = TRUE;
return $output;
}
这里面注意缓存的相关代码,Drupal缓存无处不在。另外需要注意的是,呈现数组,就是一个树状结构,一个枝干下面会有子枝干,子枝干下面又有子枝干,一直递归下去,最后是树叶。将呈现数组转为HTML的时候,也是这样递归调用的,最先转成HTML的,就是最小的单元组成部分,慢慢地合成,最后整个呈现数组彻底转为HTML。
Drupal版本:
16.5 drupal_page_footer负责收尾工作
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
当Drupal执行完HTTP请求后,调用drupal_page_footer。
/**
* Performs end-of-request tasks.
*
* This function sets the page cache if appropriate, and allows modules to
* react to the closing of the page by calling hook_exit().
*/
function drupal_page_footer() {
global $user;
module_invoke_all('exit');
// Commit the user session, if needed.
drupal_session_commit();
if (variable_get('cache', 0) && ($cache = drupal_page_set_cache())) {
drupal_serve_page_from_cache($cache);
}
else {
ob_flush();
}
_registry_check_code(REGISTRY_WRITE_LOOKUP_CACHE);
drupal_cache_system_paths();
module_implements_write_cache();
system_run_automated_cron();
}
这里提供了一个hook_exit钩子函数,允许第三方模块在HTTP请求结束时,与Drupal进行交互。然后就是会话提交,页面缓存设置。这里的ob_flush,用来刷新输出缓冲区,可以看作引导指令页面头部阶段ob_start()的一个回应。
再往下面就是注册表检查、缓存、自动运行定时任务。我们看到,定时任务的运行,是在HTTP请求结束后,运行的,这样就不会影响返回当前页面的性能。
通过阅读Drupal核心的代码,我们弄明白了,Drupal一个普通节点页面的生成过程。如果你还有不明白的地方,可以多看几遍,把每个函数都认真的读一遍,遇到不懂的函数,查一下文档。
Drupal版本:
2 引导指令分析
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
你是不是觉得,你已经学会了?还是觉得,我想知道背后发生了什么?四行代码的背后,Drupal都做了什么。这四行代码里面,前面两行代码,都是做的准备工作,里面没有什么弯弯绕绕,很好理解。我们来看第三行,drupal_bootstrap(DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL),打开includes目录下面的bootstrap.inc文件,找到drupal_bootstrap函数。
Drupal版本:
2.1 drupal_bootstrap
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
/**
* Ensures Drupal is bootstrapped to the specified phase.
*
* In order to bootstrap Drupal from another PHP script, you can use this code:
* @code
* define('DRUPAL_ROOT', '/path/to/drupal');
* require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/bootstrap.inc';
* drupal_bootstrap(DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL);
* @endcode
*
* @param $phase
* A constant telling which phase to bootstrap to. When you bootstrap to a
* particular phase, all earlier phases are run automatically. Possible
* values:
* - DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_CONFIGURATION: Initializes configuration.
* - DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_CACHE: Tries to serve a cached page.
* - DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_DATABASE: Initializes the database layer.
* - DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_VARIABLES: Initializes the variable system.
* - DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_SESSION: Initializes session handling.
* - DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_HEADER: Sets up the page header.
* - DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_LANGUAGE: Finds out the language of the page.
* - DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL: Fully loads Drupal. Validates and fixes input
* data.
* @param $new_phase
* A boolean, set to FALSE if calling drupal_bootstrap from inside a
* function called from drupal_bootstrap (recursion).
*
* @return
* The most recently completed phase.
*/
function drupal_bootstrap($phase = NULL, $new_phase = TRUE) {
// Not drupal_static(), because does not depend on any run-time information.
static $phases = array(
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_CONFIGURATION,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_CACHE,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_DATABASE,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_VARIABLES,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_SESSION,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_HEADER,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_LANGUAGE,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL,
);
// Not drupal_static(), because the only legitimate API to control this is to
// call drupal_bootstrap() with a new phase parameter.
static $final_phase;
// Not drupal_static(), because it's impossible to roll back to an earlier
// bootstrap state.
static $stored_phase = -1;
// When not recursing, store the phase name so it's not forgotten while
// recursing.
if ($new_phase) {
$final_phase = $phase;
}
if (isset($phase)) {
// Call a phase if it has not been called before and is below the requested
// phase.
while ($phases && $phase > $stored_phase && $final_phase > $stored_phase) {
$current_phase = array_shift($phases);
// This function is re-entrant. Only update the completed phase when the
// current call actually resulted in a progress in the bootstrap process.
if ($current_phase > $stored_phase) {
$stored_phase = $current_phase;
}
switch ($current_phase) {
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_CONFIGURATION:
_drupal_bootstrap_configuration();
break;
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_CACHE:
_drupal_bootstrap_page_cache();
break;
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_DATABASE:
_drupal_bootstrap_database();
break;
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_VARIABLES:
_drupal_bootstrap_variables();
break;
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_SESSION:
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/' . variable_get('session_inc', 'includes/session.inc');
drupal_session_initialize();
break;
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_HEADER:
_drupal_bootstrap_page_header();
break;
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_LANGUAGE:
drupal_language_initialize();
break;
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL:
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/common.inc';
_drupal_bootstrap_full();
break;
}
}
}
return $stored_phase;
}
在函数的注释里面,我们看到,Drupal的引导指令分为多个阶段,DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL是最后一个阶段,启动Drupal引导指令的时候,可以指定具体的阶段,而不是仅仅限于最后这个阶段。
如果要在别的PHP脚本中,启动Drupal引导指令的话,可以使用下面的代码:
define('DRUPAL_ROOT', '/path/to/drupal');
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/bootstrap.inc';
drupal_bootstrap(DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL);
我们来看函数里面的代码,首先是:
static $phases = array(
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_CONFIGURATION,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_CACHE,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_DATABASE,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_VARIABLES,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_SESSION,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_HEADER,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_LANGUAGE,
DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL,
);
这里面列出来了,引导指令的所有阶段,我们在think in Drupal的第一集里面,介绍过这些阶段。我们看到,这些阶段都是使用的大写字母,表示这是定义好的常量。在bootstrap.inc文件中,有这样的代码。
/**
* First bootstrap phase: initialize configuration.
*/
define('DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_CONFIGURATION', 0);
/**
* Second bootstrap phase: try to serve a cached page.
*/
define('DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_CACHE', 1);
/**
* Third bootstrap phase: initialize database layer.
*/
define('DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_DATABASE', 2);
/**
* Fourth bootstrap phase: initialize the variable system.
*/
define('DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_VARIABLES', 3);
/**
* Fifth bootstrap phase: initialize session handling.
*/
define('DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_SESSION', 4);
/**
* Sixth bootstrap phase: set up the page header.
*/
define('DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_HEADER', 5);
/**
* Seventh bootstrap phase: find out language of the page.
*/
define('DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_LANGUAGE', 6);
/**
* Final bootstrap phase: Drupal is fully loaded; validate and fix input data.
*/
define('DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL', 7);
我们看到这些常量,从上到下,分别对应于0、1、2、3、4、5、6、7。引导指令共分为8个阶段。当我们明白了这些常量就是整数的时候,理解下面的这段代码,就很简单了。
while ($phases && $phase > $stored_phase && $final_phase > $stored_phase) {
这句话的意思使用,如果传过来的阶段为7,那么系统将会从0开始,1,2,3,4,5,6这样一直执行下去,直到执行到阶段7为止。如果传过来的阶段为3,那么将会执行0,1,2,3。就是说,从0开始,一直执行到传递过来阶段为止。引导指令是按照先后顺序,依次执行的。
Drupal版本:
3 配置阶段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们来看阶段0,也就是配置阶段,对应的代码:
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_CONFIGURATION:
_drupal_bootstrap_configuration();
break;
我们看到,Drupal将这个阶段要做的工作,委托给了_drupal_bootstrap_configuration函数。这个函数就位于bootstrap.inc文件中,我们通过文本查找,很快就找到了这个函数的定义:
/**
* Sets up the script environment and loads settings.php.
*/
function _drupal_bootstrap_configuration() {
// Set the Drupal custom error handler.
set_error_handler('_drupal_error_handler');
set_exception_handler('_drupal_exception_handler');
drupal_environment_initialize();
// Start a page timer:
timer_start('page');
// Initialize the configuration, including variables from settings.php.
drupal_settings_initialize();
}
在这个函数里面,做了这样几件事情,设置Drupal自定义的错误处理器;Drupal环境的初始化;初始化配置,加载settings.php文件中的变量。timer_start这个函数,我也没有弄明白是做什么的,这里的字面意思是说,启动一个页面计时器。对于这个阶段,我们只需要知道,这里面做了环境初始化和加载settings.php文件两样工作就可以了。
Drupal版本:
4 页面缓存阶段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们来看阶段1,也就是页面缓存阶段,对应的代码:
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_CACHE:
_drupal_bootstrap_page_cache();
break;
Drupal将这个阶段要做的工作,委托给了_drupal_bootstrap_page_cache函数。这个函数也位于bootstrap.inc文件中,我们通过文本查找,很快就找到了这个函数的定义:
/**
* Attempts to serve a page from the cache.
*/
function _drupal_bootstrap_page_cache() {
global $user;
// Allow specifying special cache handlers in settings.php, like
// using memcached or files for storing cache information.
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/cache.inc';
foreach (variable_get('cache_backends', array()) as $include) {
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/' . $include;
}
// Check for a cache mode force from settings.php.
if (variable_get('page_cache_without_database')) {
$cache_enabled = TRUE;
}
else {
drupal_bootstrap(DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_VARIABLES, FALSE);
$cache_enabled = variable_get('cache');
}
drupal_block_denied(ip_address());
// If there is no session cookie and cache is enabled (or forced), try
// to serve a cached page.
if (!isset($_COOKIE[session_name()]) && $cache_enabled) {
// Make sure there is a user object because its timestamp will be
// checked, hook_boot might check for anonymous user etc.
$user = drupal_anonymous_user();
// Get the page from the cache.
$cache = drupal_page_get_cache();
// If there is a cached page, display it.
if (is_object($cache)) {
header('X-Drupal-Cache: HIT');
// Restore the metadata cached with the page.
$_GET['q'] = $cache->data['path'];
drupal_set_title($cache->data['title'], PASS_THROUGH);
date_default_timezone_set(drupal_get_user_timezone());
// If the skipping of the bootstrap hooks is not enforced, call
// hook_boot.
if (variable_get('page_cache_invoke_hooks', TRUE)) {
bootstrap_invoke_all('boot');
}
drupal_serve_page_from_cache($cache);
// If the skipping of the bootstrap hooks is not enforced, call
// hook_exit.
if (variable_get('page_cache_invoke_hooks', TRUE)) {
bootstrap_invoke_all('exit');
}
// We are done.
exit;
}
else {
header('X-Drupal-Cache: MISS');
}
}
}
很多人经常抱怨Drupal的性能,但是我们看到,在Drupal引导指令的第2个阶段,就支持了页面缓存。这段代码的意思是说,如果存在缓存:
$user = drupal_anonymous_user();
// Get the page from the cache.
$cache = drupal_page_get_cache();
// If there is a cached page, display it.
if (is_object($cache)) {
那么就把缓存页面,返回给客户端:
drupal_serve_page_from_cache($cache);
除此之外,还做了一些其它工作,从缓存中恢复元数据,设置默认时区,当然,(有可能)还触发了两个钩子函数:
bootstrap_invoke_all('boot');
bootstrap_invoke_all('exit');
hook_boot和hook_exit有可能在这里触发。触发钩子函数的途径很多,比如module_invoke_all、module_invoke、drupal_alter、module_implements等等。bootstrap_invoke_all是用来在引导指令阶段就触发钩子函数。
在这个函数里面,我们来看前面几句代码:
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/cache.inc';
foreach (variable_get('cache_backends', array()) as $include) {
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/' . $include;
}
这段代码的含义是,加载includes/cache.inc文件;如果cache_backends不为空的话,那么尝试加载对应include文件。这段代码,我以前很难理解,后来在Drupal实战一书里面,使用memcached模块的时候,才明白这里的用法。我们在使用memcached模块的时候,需要修改settings.php文件,对应的配置如下:
$conf['cache_backends'][] = 'sites/all/modules/memcache/memcache.inc';
$conf['cache_default_class'] = 'MemCacheDrupal';
$conf['cache_class_cache_form'] = 'DrupalDatabaseCache';
这里面有$conf['cache_backends'][],它就对应于页面缓存阶段的variable_get('cache_backends'', array())。
我们看到,Drupal与其它缓存技术的集成,是不需要去修改Drupal核心代码的,Drupal核心本身就支持这些潜在的缓存技术。当我们了解到Drupal提供的各种缓存后,我们对于Drupal的性能问题,就没有必要再去担心什么了。
Drupal版本:
5 数据库阶段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们来看阶段2,也就是数据库阶段,对应的代码:
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_DATABASE:
_drupal_bootstrap_database();
break;
Drupal将这个阶段要做的工作,委托给了__drupal_bootstrap_database函数。这个函数就位于bootstrap.inc文件中,我们通过文本查找,很快就找到了这个函数的定义:
/**
* Initializes the database system and registers autoload functions.
*/
function _drupal_bootstrap_database() {
// Redirect the user to the installation script if Drupal has not been
// installed yet (i.e., if no $databases array has been defined in the
// settings.php file) and we are not already installing.
if (empty($GLOBALS['databases']) && !drupal_installation_attempted()) {
include_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/install.inc';
install_goto('install.php');
}
// The user agent header is used to pass a database prefix in the request when
// running tests. However, for security reasons, it is imperative that we
// validate we ourselves made the request.
if ($test_prefix = drupal_valid_test_ua()) {
// Set the test run id for use in other parts of Drupal.
$test_info = &$GLOBALS['drupal_test_info'];
$test_info['test_run_id'] = $test_prefix;
$test_info['in_child_site'] = TRUE;
foreach ($GLOBALS['databases']['default'] as &$value) {
// Extract the current default database prefix.
if (!isset($value['prefix'])) {
$current_prefix = '';
}
elseif (is_array($value['prefix'])) {
$current_prefix = $value['prefix']['default'];
}
else {
$current_prefix = $value['prefix'];
}
// Remove the current database prefix and replace it by our own.
$value['prefix'] = array(
'default' => $current_prefix . $test_prefix,
);
}
}
// Initialize the database system. Note that the connection
// won't be initialized until it is actually requested.
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/database/database.inc';
// Register autoload functions so that we can access classes and interfaces.
// The database autoload routine comes first so that we can load the database
// system without hitting the database. That is especially important during
// the install or upgrade process.
spl_autoload_register('drupal_autoload_class');
spl_autoload_register('drupal_autoload_interface');
}
这个函数代码里面的第一部分,当数据库为空,当前尚未安装Drupal的时候,此时做了重定向,重定向到了install.php页面。
if (empty($GLOBALS['databases']) && !drupal_installation_attempted()) {
include_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/install.inc';
install_goto('install.php');
}
这个函数代码里面的第二部分,表示如果当前为单元测试环境下,要做的工作,我们这里不是单元测试环境,所以不需要考虑这段代码的含义:
if ($test_prefix = drupal_valid_test_ua()) {
…
}
再往下,是加载includes/database/database.inc文件,这样就可以建立数据库连接了。最后是自动加载(缓加载)。
spl_autoload_register('drupal_autoload_class');
spl_autoload_register('drupal_autoload_interface');
我们这里看到,Drupal7只支持类、接口的缓加载,不支持函数的缓加载。我第一集里面讲过这个问题,今天看到的是对应的代码部分。
Drupal版本:
6 变量阶段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们来看阶段3,也就是变量阶段,对应的代码:
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_VARIABLES:
_drupal_bootstrap_variables();
break;
Drupal将这个阶段要做的工作,委托给了_drupal_bootstrap_variables函数。这个函数就位于bootstrap.inc文件中,我们通过文本查找,很快就找到了这个函数的定义:
/**
* Loads system variables and all enabled bootstrap modules.
*/
function _drupal_bootstrap_variables() {
global $conf;
// Initialize the lock system.
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/' . variable_get('lock_inc', 'includes/lock.inc');
lock_initialize();
// Load variables from the database, but do not overwrite variables set in settings.php.
$conf = variable_initialize(isset($conf) ? $conf : array());
// Load bootstrap modules.
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/module.inc';
module_load_all(TRUE);
}
首先是加载includes/lock.inc文件,并初始化锁系统。接着是变量的初始化,我们知道,Drupal中很多配置变量都是存放在variable表里面,这里的初始化,将会把这个表中的数据全部加载出来的,是的,整张表的数据。我们平时做开发的时候,不要在变量里面存储大数据,这是我们要注意的。
当我看到lock_initialize的时候,我当时想,我只知道Drupal里面有锁机制,但是从来不知道具体的用处。我今天在写文档的时候,顺着查看了一下API函数,也就是查看了一下variable_initialize函数,一下明白了锁机制的用法,同时也明白了为什么这里需要加载includes/lock.inc文件。
function variable_initialize($conf = array()) {
// NOTE: caching the variables improves performance by 20% when serving
// cached pages.
if ($cached = cache_get('variables', 'cache_bootstrap')) {
$variables = $cached->data;
}
else {
// Cache miss. Avoid a stampede.
$name = 'variable_init';
if (!lock_acquire($name, 1)) {
// Another request is building the variable cache.
// Wait, then re-run this function.
lock_wait($name);
return variable_initialize($conf);
}
else {
// Proceed with variable rebuild.
$variables = array_map('unserialize', db_query('SELECT name, value FROM {variable}')->fetchAllKeyed());
cache_set('variables', $variables, 'cache_bootstrap');
lock_release($name);
}
}
foreach ($conf as $name => $value) {
$variables[$name] = $value;
}
return $variables;
}
db_query负责将变量从数据库表中取出,array_map('unserialize',..)负责反序列化。lock_acquire尝试获取锁,获取失败就等待一下lock_wait;获取成功后,就释放锁lock_release。此外,我们看到,所有的变量都存放在一个大的数组里面,名值对。
module_load_all(TRUE),这句代码,负责加载引导指令阶段,需要加载的module文件。我们知道,Drupal启动后,会加载所有的module文件。不过在启动的过程中,也就是在引导指令阶段,就有一部分module文件被优先加载了进来。使用phpmyadmin打开Drupal的数据库,找到system表,打开这个表,我们看到这个表里面包含了bootstrap一列。

凡是这里bootstrap的值为1的模块,都会在module_load_all(TRUE)的时候加载进来。哪些模块的bootstrap的值为1呢?
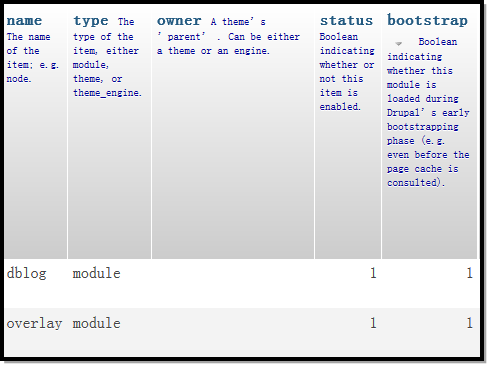
默认只有这么两个模块。我当时还想着比如system、user模块会被加载进来,没有想到是这两个模块。
Drupal版本:
7 会话阶段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们来看阶段4,也就是会话阶段,对应的代码:
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_SESSION:
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/' . variable_get('session_inc', 'includes/session.inc');
drupal_session_initialize();
break;
在这里,首先加载includes/session.inc 文件,然后调用drupal_session_initialize函数。drupal_session_initialize函数就位于includes/session.inc文件中,我们通过文本查找,很快就找到了这个函数的定义:
/**
* Initializes the session handler, starting a session if needed.
*/
function drupal_session_initialize() {
global $user, $is_https;
session_set_save_handler('_drupal_session_open', '_drupal_session_close', '_drupal_session_read', '_drupal_session_write', '_drupal_session_destroy', '_drupal_session_garbage_collection');
// We use !empty() in the following check to ensure that blank session IDs
// are not valid.
if (!empty($_COOKIE[session_name()]) || ($is_https && variable_get('https', FALSE) && !empty($_COOKIE[substr(session_name(), 1)]))) {
// If a session cookie exists, initialize the session. Otherwise the
// session is only started on demand in drupal_session_commit(), making
// anonymous users not use a session cookie unless something is stored in
// $_SESSION. This allows HTTP proxies to cache anonymous pageviews.
drupal_session_start();
if (!empty($user->uid) || !empty($_SESSION)) {
drupal_page_is_cacheable(FALSE);
}
}
else {
// Set a session identifier for this request. This is necessary because
// we lazily start sessions at the end of this request, and some
// processes (like drupal_get_token()) needs to know the future
// session ID in advance.
$GLOBALS['lazy_session'] = TRUE;
$user = drupal_anonymous_user();
// Less random sessions (which are much faster to generate) are used for
// anonymous users than are generated in drupal_session_regenerate() when
// a user becomes authenticated.
session_id(drupal_hash_base64(uniqid(mt_rand(), TRUE)));
if ($is_https && variable_get('https', FALSE)) {
$insecure_session_name = substr(session_name(), 1);
$session_id = drupal_hash_base64(uniqid(mt_rand(), TRUE));
$_COOKIE[$insecure_session_name] = $session_id;
}
}
date_default_timezone_set(drupal_get_user_timezone());
}
session_set_save_handler用来初始化会话处理器,包括会话的打开、关闭、读取、写入、销毁、垃圾收集。接下来检查会话是否存在,如果会话已经存在,那么启动会话;如果会话不存在,那么生成会话。我们这里看到函数drupal_hash_base64,这是Drupal的加密算法,采用base64的哈希算法。uniqid用来生成一个唯一的ID号。session_id用来设置会话的ID号。
Drupal版本:
8 页面头部阶段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们来看阶段5,也就是页面头部阶段,对应的代码:
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_PAGE_HEADER:
_drupal_bootstrap_page_header();
break;
在这里,Drupal将这个阶段的工作委托给了_drupal_bootstrap_page_header函数。我们通过文本查找,很快就找到了这个函数的定义:
/**
* Invokes hook_boot(), initializes locking system, and sends HTTP headers.
*/
function _drupal_bootstrap_page_header() {
bootstrap_invoke_all('boot');
if (!drupal_is_cli()) {
ob_start();
drupal_page_header();
}
}
在这个函数里,首先是触发hook_boot;接着使用drupal_is_cli判断一下,当前脚本是否是运行在命令行环境下。我们这里当然不是。如果不是的话,使用ob_start来打开输出缓冲区,这是服务器端和浏览器端交互时,常见的PHP用法,接着使用drupal_page_header输出页面头部信息。什么是页面头部信息,我们来看一下这个帮助函数:
function drupal_page_header() {
$headers_sent = &drupal_static(__FUNCTION__, FALSE);
if ($headers_sent) {
return TRUE;
}
$headers_sent = TRUE;
$default_headers = array(
'Expires' => 'Sun, 19 Nov 1978 05:00:00 GMT',
'Last-Modified' => gmdate(DATE_RFC1123, REQUEST_TIME),
'Cache-Control' => 'no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0',
'ETag' => '"' . REQUEST_TIME . '"',
);
drupal_send_headers($default_headers);
}
这里面的'Expires'、'Last-Modified'、'Cache-Control'、'ETag'就是页面头部信息,对于登陆用户,Drupal总是将缓存设置为no-cache,这样保证登陆用户每次请求总能看到最新的页面。
Drupal版本:
9 语言阶段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们来看阶段6,也就是语言阶段,对应的代码:
case DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_LANGUAGE:
drupal_language_initialize();
break;
在这里,Drupal将这个阶段的工作委托给了drupal_language_initialize函数。我们通过文本查找,很快就找到了这个函数的定义:
/**
* Initializes all the defined language types.
*/
function drupal_language_initialize() {
$types = language_types();
// Ensure the language is correctly returned, even without multilanguage
// support. Also make sure we have a $language fallback, in case a language
// negotiation callback needs to do a full bootstrap.
// Useful for eg. XML/HTML 'lang' attributes.
$default = language_default();
foreach ($types as $type) {
$GLOBALS[$type] = $default;
}
if (drupal_multilingual()) {
include_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/language.inc';
foreach ($types as $type) {
$GLOBALS[$type] = language_initialize($type);
}
// Allow modules to react on language system initialization in multilingual
// environments.
bootstrap_invoke_all('language_init');
}
}
在这里,language_types函数用来获取所有的语言类型;language_default函数用来获取默认语言。这里的语言类型包括三类:
/**
* The type of language used to define the content language.
*/
define('LANGUAGE_TYPE_CONTENT', 'language_content');
/**
* The type of language used to select the user interface.
*/
define('LANGUAGE_TYPE_INTERFACE', 'language');
/**
* The type of language used for URLs.
*/
define('LANGUAGE_TYPE_URL', 'language_url');
我刚开始以为,这里是获取所有的语言呢。后来往下细看了一下,原来的想法不对。注意这里是语言类型,它里面包括三种类型,界面、内容、URL。drupal_multilingual用来判断是否是多语言,判断的标准是启用的语言数量是否大于1,对于中文用户来说,我们通常启用简体中文,以及默认的英文,所以这里的判断应该为真。再往下就是加载includes/language.inc,为每种语言类型初始化。最后触发hook_language_init,给第三方模块一个交互的机会。
Drupal版本:
1路径分析
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
当我们访问node/1这个路径的时候,会发生什么呢?首先我们看到的路径,通常是这样的形式:
此时,我们是启用了简洁URL的,如果没有启用的话,可以配置,网上有比较多的教程。不启用简洁URL的路径,则是这样的:
http://www.example.com/?q=node/1
是的,与前者相比,多了一个“?q=”。
这是我们看到的路径,也是Apache看到的路径。可能有人会问,难道Drupal看到的路径不是这个样子的?是的,Drupal看到的路径不是这个样子。那么可能还会有人继续问,Drupal看到的路径是什么?Drupal看到的路径是这个样子的:
http://www.example.com/index.php?q=node/1
别名模式下:
http://www.example.com/index.php?q=aboutus
我们在本地做一个实验,分别访问路径:
http://localhost/snt6/index.php?q=node/1
http://localhost/snt6/?q=node/1
我们看到了什么?我们看到的内容是完全一样的。aboutus和node/1之间是别名关系,可以说是一一对应的关系,Drupal在数据库里面,有张表,用来存储这样的对应关系。当我们访问路径aboutus的时候,它自动的就找到了对应的内部路径node/1。这个我们比较好理解。对于很多人,他刚开始的时候,并不知道Drupal看到的路径是:
http://www.example.com/index.php?q=node/1
很多人可能有个误区,感觉我们看到的路径,就是Drupal看到的路径。这样理解是有问题的。
当我们使用
http://www.example.com/?q=node/1
访问页面时,Apache帮我们做了转换,它将这个路径转为了:
http://www.example.com/index.php?q=node/1
在简洁URL下,apache将路径http://www.example.com/node/1最终也会转为:
http://www.example.com/index.php?q=node/1
有人可能会问,你是怎么知道这个转换的?在Drupal的根目录下,有这样一个文件.htaccess。我们打开这个文件,里面有这行代码:
# Pass all requests not referring directly to files in the filesystem to
# index.php. Clean URLs are handled in drupal_environment_initialize().
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !=/favicon.ico
RewriteRule ^ index.php [L]
这段代码就是做这个转换的,这段代码里面的RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f是什么意思?这个我也不知道。我们只需要知道,这里做了一个路径转换。仅此而已。
Drupal版本:
1.1 index.php文件
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们看到的,几乎所有的Drupal页面,入口程序都是index.php。当然也有例外,比如安装Drupal时,会使用install.php,更新Drupal时,会使用update.php。例外的情况,我们这里就不分析了,我们来分析一下正常的情况。
我们打开Drupal根目录下的index.php程序,我们看到了非常简洁的代码:
<?php
/**
* @file
* The PHP page that serves all page requests on a Drupal installation.
*
* The routines here dispatch control to the appropriate handler, which then
* prints the appropriate page.
*
* All Drupal code is released under the GNU General Public License.
* See COPYRIGHT.txt and LICENSE.txt.
*/
/**
* Root directory of Drupal installation.
*/
define('DRUPAL_ROOT', getcwd());
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/bootstrap.inc';
drupal_bootstrap(DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL);
menu_execute_active_handler();
老外写代码,通常是注释比代码长,这个文件也不例外。上面的注释说,Drupal所有的页面,都走这个入口程序。路由系统,将会把控制权分发给对应的处理器,然后输出对应的页面。我们往下看代码,第一行:
define('DRUPAL_ROOT', getcwd());
这里面定义了一个常量,DRUPAL_ROOT。getcwd,用来获取当前文件所在的目录,比如我们这里就是D:\xampp\htdocs\snt6。
第二行代码:
require_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/bootstrap.inc';
这段代码的作用,是加载bootstrap.inc文件。
第三行代码:
drupal_bootstrap(DRUPAL_BOOTSTRAP_FULL);
这段代码的作用,是启动Drupal,说的更完整一点就是启用Drupal的完整引导指令。drupal_bootstrap这个函数,位于bootstrap.inc文件中,我们前面加载这个文件,就是为了执行这个函数。这里的引导指令,是每个Drupal页面,都要走过的流程。这就有点类似于,我们打开计算机的时候,点了启动按钮,点过之后,计算机需要一个启动的过程,这个电脑的开机启动过程,就类似于Drupal的引导指令。
第四行代码:
menu_execute_active_handler();
这个函数做了什么?连个参数都没有。前面Drupal已经启动了,跑了起来,这个函数的作用是这样的,根据Drupal看到的路径,找到对应的回调函数,调用对应的回调函数,然后将返回的内容,组装成HTML页面,返回给浏览器。也就是英文注释里面所讲的。
这就是Drupal的组装过程,非常简单。与其它系统不一样,Drupal只有一个入口程序,我见过的一些系统都是这样的:
http://www.example.com/foroum.php
http://www.example.com/login.php
http://www.example.com/user/register.php
只有Drupal,是一个入口程序。

index.php文件的逻辑结构