第1章 实体(Entity)API
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
节点系统,在Drupal里面的历史悠久,是很早很早以前,就有了的一种机制。慢慢的,围绕着节点系统,出现了Flexinode,我们看这个模块的创建日期,2004年2月8日,快9年了,Flexinode允许用户创建新的内容类型,并为内容类型添加字段,随着技术的进步, Flexinode的实现机制跟不上了发展的需要;两年后,也就是2006年,出现了CCK模块,此时Drupal的版本还是4.7;随后,CCK取代了Flexinode,发展成为了Drupal5、Drupal6下面的标准实现;并最终进入了Drupal7的内核,当然进入Drupal7后,名字改为了Field。
在Drupal5、 Drupal6下面,随着CCK的日趋流行,它给节点系统带来了极大的灵活性,在Drupal 5、 Drupal6两个版本下,CCK是仅支持节点系统的。在Drupal社区当中,一种声音愈来愈强,这就是将评论、区块、用户Profile以及很多其它系统,转为节点系统的声音。读过Drupal专业开发指南中文版的用户,在里面的节点系统一章,讲过一个问题,不是一切东西都是节点,里面讲述了为什么不把评论处理成为节点,很多人都知道这个道理,但是把所有系统,向节点系统靠拢的趋势,一直存在着,并且影响越来越广。为什么会这样?因为CCK模块的存在,使得节点系统非常的灵活。
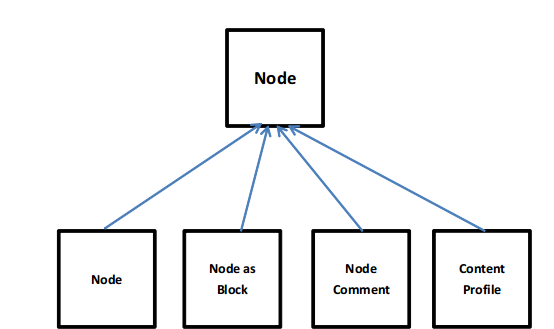
在这种趋势的影响下,出现了Node as Block、Node comment、Content Profile等流行模块,它们将区块、评论、profile建立在了节点系统之上,这样就可以方便的利用CCK了。随着,这些模块的流行,人们也逐渐的意识到了,这种方式的局限性。有哪些局限性呢?在节点系统中,除了CCK字段以外,它还有自己属性,比如作者、创建日期、修改日期、标题、nid、置顶、推到首页…等等,很多这样的属性,这些属性对于其它系统可能是多余的无用的,所以人们还需要编写模块来隐藏这些属性,或者自动设置某些属性,比如对于标题,就存在一个Automatic Nodetitles,帮助用户隐藏多余的标题。
Drupal版本:
1 实体
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
在CCK进入Drupal7内核的时候,很多人进一步思考的CCK的优势,并且认识到,很多其它的系统,比如用户系统、分类系统、评论系统,也都存在利用CCK的需求。因此,在Drupal7下,对CCK模块做了进一步的扩充,并将其更名为Field模块,使得用户可以向节点、评论、分类术语、用户上面添加字段。而这种扩充的结果,就是引入了实体(Entity)这样的一个概念,实体是伴随着Field进入Drupal内核,而衍生抽象出来的一个概念。什么是实体呢?这种概念性质的东西,不是一句话就理解透的,我们看看例子: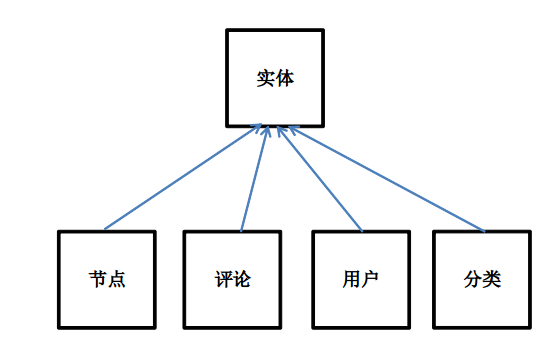
在Drupal7下,节点、评论、用户、分类都是实体的一种。对于实体,在Drupal7下面,我们可以这样理解,具有相同属性,并且可以为它添加字段的一种东西。当然,有些实体,是不能够向它们上面添加字段的,这种情况也是存在的。当我们定义一种实体的时候,可以为它定义一组公用的属性,然后基于Field模块,可以为其添加各种字段。我们可以看到,评论,它是一种实体,所有的评论对象都具有公用的一组属性,由于可以往实体上面添加字段,所以我们这里,就不存在把评论系统建立在节点系统之上的问题了,我们这里既利用了Field模块的灵活性,也不用额外的处理并不属于该类实体的属性。这是一个进步。
Drupal版本:
10 总结
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
通过本章的学习,我们学到了以下内容:
(1),什么是实体,实体在Drupal7中的重要地位
(2),如何基于Entity API自定义一个实体类型
(3),EntityFieldQuery的介绍、使用
Drupal版本:
2 Bundle(包)
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
伴随着,实体的出现,还出现了另一个概念,Bundle,中文可以翻译为“包”。什么是Bundle呢,我们可把它看作,一种实体下面的一个具体实现。以节点为例: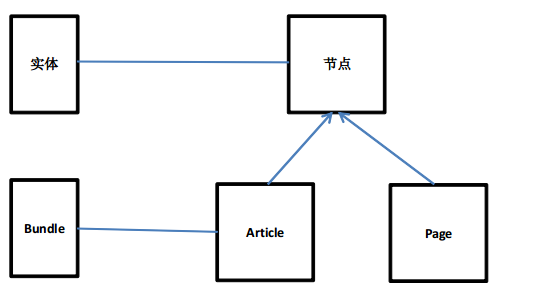
Drupal7核心内置的两种内容类型: Article、Page,就是一种Bundle。我们可以把Bundle看作,是Drupal7下面,对内容类型的一种概念上的扩展。对于分类来讲,一个词汇表,就是一个Bundle。在Profile2下面,我们可以为不同的角色定义不同的Profile,比如学生所用的Profile、教师所用的Profile,这些也是一种Bundle。
在同一种实体下面,不同Bundle之间,它们的属性是通用的,但是可以有不同的默认配置;它们的字段,则可以分别添加,不同的Bundle,可以为其添加不同的字段,当然两个Bundle,我们为其添加了相同的字段,这也是允许的。
Drupal版本:
3 不是所有的东西都是实体
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
现在,节点、分类术语、评论、用户都统一到了实体上来了,这是不是意味着说,所有的东西都是实体呢?当然不是。在Drupal7的核心系统里面,区块系统就不是实体,菜单系统也不是实体,因此,我们可以说,不是所有的东西都是实体。但是这些东西,正在被转为实体,比如区块,现在有一个第三方模块bean,全称为“Block Entities Aren't Nodes” “区块实体不是节点”,此外,在Drupal8的核心开发里面,菜单连接,也正在被转为实体。此外,比如webform模块,一直都是非常流行的,但是到了Drupal7下面,出现了Entity form模块,与之竞争,将来webform是否会被Entity form模块所取代,这个现在还不好判断。比如在Ubercart、Commerce里面,订单,都已经被处理成为了实体,而在Commerce里面,产品、客户信息都已被处理成为实体。还有我们提到过的,Field Collection模块,字段实体的出现,更是扩展了实体的应用范围。
因此,我们可以这样说,不是所有的东西,都是实体;但是所有的东西,都可以转为实体,只要你去转,都可以转过来。
Drupal版本:
4 Drupal7核心实体API介绍
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
在Drupal7中,核心的实体系统,存放在includes下面的entity.inc文件中,这里面,包含一个DrupalEntityControllerInterface接口、DrupalDefaultEntityController类、EntityFieldQueryException类、EntityFieldQuery类、EntityMalformedException类。所有的实体,必须实现DrupalEntityControllerInterface接口,对于我们常见的大多数实体,只需要继承DrupalDefaultEntityController类即可,如果需要实现的实体不是存放在数据库中的,此时则需要单独的实现DrupalEntityControllerInterface接口。EntityFieldQuery对Entity Field的SQL查询做了封装,当然,封装的不是很彻底,有很多的局限性,对于我们常见的查询,尤其涉及到字段的,用起来非常方便。我们在本章会对EntityFieldQuery做专门的介绍。
在commons.inc文件中,定义了一组与实体相关的API函数:
|
函数名 |
用途描述 |
|
entity_create_stub_entity |
帮助函数,用来组装一个带有初始ids的对象结构。 |
|
entity_extract_ids |
帮助函数,用来从一个实体中提取id、vid、bundle等信息。 |
|
entity_form_field_validate |
把字段API验证附加到实体表单上。 |
|
entity_form_submit_build_entity |
对于简单的实体表单,这个函数可以用来将表单提交的值复制到实体属性上面来。 |
|
entity_get_controller |
获取某一实体类型的实体控制器类。 |
|
entity_get_info |
获取某一实体类型的实体信息数组。 |
|
entity_info_cache_clear |
重置有关实体类型的缓存信息。 |
|
entity_label |
返回实体的标签。 |
|
entity_language |
返回实体的语言。 |
|
entity_load |
从数据库中加载实体。 |
|
entity_load_unchanged |
从数据库中加载未被修改了的实体。 |
|
entity_prepare_view |
用来触发钩子hook_entity_prepare_view() |
|
entity_uri |
返回实体的URI元素。 |
我们看到,Drupal7里面,与实体相关的API函数放在了commons.inc文件中,这是一个权宜之计。在Drupal8里面,这些相关的函数都被放到了entity.inc文件中去了。
Drupal核心,包含了与实体相关的钩子函数,这些钩子函数,允许我们在实体生命周期的各个不同阶段,与之交互。我们来看一下这些钩子函数。我们可以在system模块里面的system.api.php文件中,找到这些钩子函数。
|
钩子 |
描述 |
|
hook_entity_delete |
实体删除时,用来交互的钩子。 |
|
hook_entity_info |
这个钩子可以用来定义一个或者多个实体类型。 |
|
hook_entity_info_alter |
用来修改hook_entity_info里面的定义信息。 |
|
hook_entity_insert |
实体插入时,用来交互的钩子。 |
|
hook_entity_load |
实体加载时,用来交互的钩子。 |
|
hook_entity_prepare_view |
准备显示实体时,用来交互的钩子。 |
|
hook_entity_presave |
在保存实体前,用来交互的钩子。 |
|
hook_entity_query_alter |
用来修改或者执行一个EntityFieldQuery。 |
|
hook_entity_update |
实体更新时,用来交互的钩子。 |
|
hook_entity_view |
在实体正在组装时,呈现(render)之前,用来交互的钩子。 |
|
hook_entity_view_alter |
用来修改ENTITY_view()的结果。 |
|
hook_entity_view_mode_alter |
用来修改正被显示的实体的查看模式。 |
Drupal版本:
5 Entity API模块
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们需要注意,模块的名字就叫Entity API,简称entity,这个名字起的够霸道的,模块的作者也很牛,就是fago,Drupal核心Entity系统的维护者。在Drupal7将要发布的时候,Fago就认识到了Drupal7里面,对实体的支持,还很不完善,他还专门写了一篇文章,指出未来的方向是实体,为此他开发了Entity API模块,作为Drupal核心实体系统的补充,Entity API模块里面的很多概念,被Fago搬到了Drupal8的内核里面了。Entity API模块做了多方面的扩展,我们这里简单了解一下。
Drupal版本:
7 定义自己的实体类型
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
其实2011年的时候,自己就想编写一个模块,定义一个实体类型,最初的想法是把区块改造为实体,我在官方网站上面搜索,发现已经有了这样的一个模块了,bean,就是这个时候冒出来的。后来想把Contact模块,重新实现为实体的形式,不过发现了有个Entity Forms模块,可以做这件事情。再往后,就想不出来哪些东西可以改造为实体了。一直到搭建网上书店时,解决面包屑问题的时候,有了将面包屑改造为实体的想法,并且在现有的模块当中,没有这样的技术实现。
在这一章中,大家跟我一道来学习一下,如何采用实体的形式来实现Drupal里面的面包屑功能。面包屑这个实体,有一点点小小的特殊,它的bundle只有一个,还是面包屑,类似于用户,实体下面的bundle只有一个。
从我的角度,推荐几个模块,供大家阅读、学习、使用,推荐的有Profile2模块,这个模块是基于Entity API模块的,很具有代表性,而且我们在实际当中,也经常用到这个模块,还有,这个模块进入了Drupal8的内核了。其次推荐Examples里面的entity_example模块,推荐model模块,这是一个基于Entity API的更简单实用的例子,只不过模块本身没有太大价值。
现有的面包屑模块很多,这里罗列一下,custom_breadcrumbs、menu_breadcrumb、path_breadcrumbs、breadcrumb、crumbs、hansel、taxonomy_breadcrumb,其中path_breadcrumbs和crumbs是后起之秀。我们这里把我们的模块的名字叫做breadcrumb2,参考一下Profile2,我在breadcrumb项目的问题列表中申请成为维护者,但是没有人回应,现在看起来需要另起炉灶了。
在我们创建模块之前,请大家把Profile2和model两个模块的代码阅读一遍,为什么呢?因为我们的很多代码都是从这里直接复制过来的。作者也是第一次创建一个实体类型,很多时候也是摸着石头过河。
Drupal版本:
7.1 Info 文件
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们创建一个breadcrumb2.info文件,输入以下内容:
name = Breadcrumb2
description = Supports configurable breadcrumbs.
core = 7.x
files[] = breadcrumb2.admin.inc
files[] = breadcrumb2.info.inc
files[] = breadcrumb2.test
dependencies[] = link
dependencies[] = rules
dependencies[] = field_validation
configure = admin/structure/breadcrumbs
这里面的键值我这里就不讲解了,我们这个模块依赖于rules、entity模块,由于rules本身依赖于entity,所以我们这里只需要依赖于rules即可。我们需要添加一个链接字段,面包屑导航里面包含的就是多个链接,所以我们这里依赖于link模块。由于我们将path,也就是内部路径,处理成为了字段的形式,所以我们需要加一些验证,也就用到了field_validation模块了。
Drupal版本:
7.10 为面包屑添加字段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
导航到admin/structure/breadcrumbs/fields,添加两个字段“Path”和“Breadcrumb Link”。这是添加好的样子:
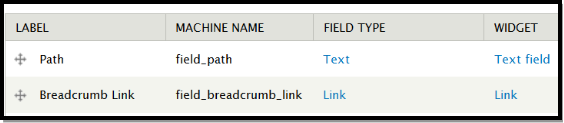
对于“Path”字段,我们将其设置为必填的,其它采用默认配置。对于“Breadcrumb Link”,选中了“Optional URL”,将“Link Title”设置为了“Required Title”,将“Number of values”设置为了“unlimited”(不限)。我们后面根据需要可能会调整这里的配置。
Drupal版本:
7.11 添加实体
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们首先定义菜单项:
$items['breadcrumb/add'] = array(
'title' => 'Add breadcrumb',
'page callback' => 'breadcrumb2_add',
'access arguments' => array('administer breadcrumbs'),
'file' => 'breadcrumb2.admin.inc',
);
接着,向breadcrumb2.admin.inc添加回调函数breadcrumb2_add:
/**
* Returns a breadcrumb submission form.
*/
function breadcrumb2_add(){
$breadcrumb = entity_get_controller('breadcrumb2')->create();
drupal_set_title(t('Create breadcrumb'));
$output = drupal_get_form('breadcrumb2_form', $breadcrumb);
return $output;
}
在这个函数里面,我们首先使用entity_get_controller创建了一个初始化的面包屑,然后设置了标题,最后调用drupal_get_form,调用的表单ID为breadcrumb2_form,同时我们把$breadcrumb传递给了它。我们这样做的目的,是希望breadcrumb2_form同时能够适应于编辑表单。我们来看看breadcrumb2_form的定义:
/**
* The breadcrumb edit form.
*/
function breadcrumb2_form($form, &$form_state, $breadcrumb) {
// Save the breadcrumb for later, in case we need it.
$form['#breadcrumb'] = $breadcrumb;
$form_state['breadcrumb'] = $breadcrumb;
$form['bid'] = array(
'#type' => 'value',
'#value' => isset($breadcrumb->bid) ? $breadcrumb->bid : NULL,
);
// Add the field related form elements.
field_attach_form('breadcrumb2', $breadcrumb, $form, $form_state);
$form['actions'] = array('#type' => 'actions');
$form['actions']['submit'] = array(
'#type' => 'submit',
'#value' => t('Save'),
'#weight' => 40,
);
if (!empty($breadcrumb->bid)) {
$form['actions']['delete'] = array(
'#type' => 'submit',
'#value' => t('Delete breadcrumb'),
'#weight' => 45,
'#limit_validation_errors' => array(),
'#submit' => array('breadcrumb2_form_submit_delete')
);
}
$form['#validate'][] = 'breadcrumb2_form_validate';
$form['#submit'][] = 'breadcrumb2_form_submit';
return $form;
}
首先,我们将$breadcrumb保存到了$form和$form_state里面,这里保存原始的面包屑对象。接着,我们添加了'bid'元素,它的类型为value,为什么这样做呢?因为有些模块会使用entity_extract_ids来提取实体的ID,在Drupal7里面,如果我们不预先保存一个实体ID的话,entity_extract_ids就会提取不出来,Drupal8已经改进了这个问题,我遇到过这个问题,所以在这里加了了'bid'。接着是使用field_attach_form,把实体上面的字段也添加进来,由于字段的添加,是动态的,我们也不知道具体有几个字段,通过field_attach_form,我们就可以把这个工作委托给Field模块了,它能够帮我们做这件事情。再往下是提交、删除按钮,我们把这两者放到了actions里面了,actions是Drupal7里面的一个新的表单元素类型;对于删除按钮,我们为它指定了一个单独的提交函数breadcrumb2_form_submit_delete,同时为它设置了'#limit_validation_errors',通过这个设置,在删除面包屑的时候,即便是存在验证错误的话,也可以正常提交。最后是为表单设置$form['#validate']、$form['#submit'],我们在第一集里面学过,即便不设置这两行代码,表单系统也会自动使用这两个函数,为什么明确的设置呢?因为我看到其它实体的添加表单都是这样明确设置的,包括节点的添加表单,或许这样做的好处的,代码的可读性更强。
接下来是表单验证函数:
function breadcrumb2_form_validate($form, &$form_state) {
$breadcrumb = $form_state['breadcrumb'];
// Notify field widgets to validate their data.
field_attach_form_validate('breadcrumb2', $breadcrumb, $form, $form_state);
}
代码比较简单,我们模块本身没有多少验证工作,所以这里直接将验证工作委托给了Field模块,这里使用的是field_attach_form_validate。
再往下,是提交函数,逻辑也比较简单:
/**
* Breadcrumb form submit handler.
*/
function breadcrumb2_form_submit($form, &$form_state) {
$breadcrumb = &$form_state['breadcrumb'];
// Notify field widgets.
field_attach_submit('breadcrumb2', $breadcrumb, $form, $form_state);
// Save the breadcrumb
breadcrumb2_save($breadcrumb);
drupal_set_message(t('Breadcrumb saved.'));
$form_state['redirect'] = 'breadcrumb/' . $breadcrumb->bid;
}
我们首先使用field_attach_submit,将提交委托给了Field模块,接着我们调用我们的API函数breadcrumb2_save,保存实体。最后设置一个消息,并重定向。
在这部分,需要注意的是field_attach_form、field_attach_form_validate、field_attach_submit的使用。这里我有个疑问,不知道为什么不把field_attach_submit叫做field_attach_form_submit。
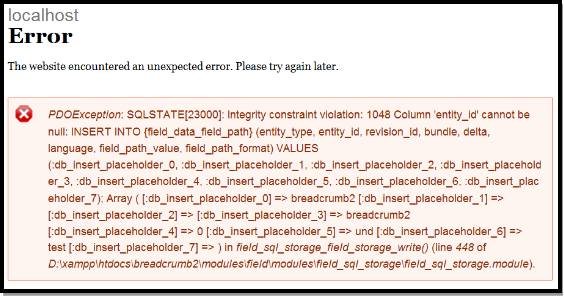
编写完这些代码以后,可以测试一下了,如果你按照这里所列的代码,跟着做的,现在访问breadcrumb/add页面,我们可以看到一个表单页面,这里面包含前面我们添加的两个字段。一切正常。输入一些测试数据,提交,我们遇到了第一个问题:

这是一个PHP错误。我在网上搜索了这个问题,很多人也遇到了同样的问题,但是没有找到答案。我们在开发的过程中,是存在一些问题,这些问题起初我也没有注意到,我也希望一次能够搞定所有的问题,但是错误总是不经意的出现。如果你能够,在现有的代码基础上,把所有的问题都解决掉,那么证明你完全掌握了如何定义一个实体类型。我也是在解决这些问题的过程中,才明白了里面的很多细微的地方。
Drupal版本:
7.12 调试并解决已有代码的问题
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
通过Google搜索,找不到答案。有很多同样的问题,但是里面没有我们想要的答案。这个时候,我们需要打开common.inc文件,找到7750行,Drupal核心的版本不一样,这里显示的行数也不一致。但是代码是一样的:
/**
* Get the entity controller class for an entity type.
*/
function entity_get_controller($entity_type) {
$controllers = &drupal_static(__FUNCTION__, array());
if (!isset($controllers[$entity_type])) {
$type_info = entity_get_info($entity_type);
//print debug($type_info);
$class = $type_info['controller class'];
//drupal_set_message('123456');
$controllers[$entity_type] = new $class($entity_type);
}
return $controllers[$entity_type];
}
当然,核心里面是没有print debug和drupal_set_message这两句的,这是我调试的时候添加了,我想查看一下$type_info里面包含哪些信息。发现这里打印出来的信息,和我们在前面定义的有出入。我首先想到的是,是不是'controller class'没有设置正确?我们需要自己定义一个控制器类?
问题1:
通过print debug,我还是发现了一个错误,在breadcrumb2_entity_info里面:
'entity keys' => array(
'id' => 'pid',
),
漏网之鱼,复制别人的代码的时候,经常会遇到这种情况,将它修正过来:
'entity keys' => array(
'id' => 'bid',
),
问题2:
将'bundle keys'注视掉,我们只有一个bundle,没有‘type’这个概念。
/*
'bundle keys' => array(
'bundle' => 'type',
),
*/
问题3:
前面的两个问题,是我重读breadcrumb2_entity_info代码以后,所做的两个修正;但是问题仍然存在。我通过进一步的测试,发现验证是正常的,问题出在了表单的提交函数里面。我把breadcrumb2_form_submit里面的代码全部注销掉,问题没有了,当然我们的面包屑实体也没有保存起来。进一步的细化,发现breadcrumb2_save($breadcrumb);出了问题。
接着检查了breadcrumb2_save的代码,里面的逻辑也非常简单,只有这么简单的一行:
return $breadcrumb->save();
在Breadcrumb里面,我们并没有定义save方法,这个方法应该是它的父类Entity定义的。所以回到Entity API模块里面查找Entity类的对应代码。此时我发现,这个类存放到了entity\includes下面的entity.inc文件中了。注意,这个文件夹下面,包含4个inc文件,分别为entity.controller.inc、entity.inc、entity.property.inc、entity.ui.inc、entity.wrapper.inc。我们打开entity.inc文件,找到save方法:
/**
* Permanently saves the entity.
*
* @see entity_save()
*/
public function save() {
return entity_get_controller($this->entityType)->save($this);
}
对这里的代码,做以下修改:
public function save() {
drupal_set_message($this->entityType);
//return entity_get_controller($this->entityType)->save($this);
}
我们去掉了实际的保存逻辑代码,加上了一个drupal_set_message,我想看看此时传递过来的实体类型到底是什么。
再次测试,发现$this->entityType的值竟然为“breadcrumb”,而实际应该为“breadcrumb2”,如果我们的模块名字为breadcrumb就好了,就不会遇到这个问题了。找到原因以后,很快就定位到了错误的代码地方,Breadcrumb的构造方法,原来为:
public function __construct($values = array()) {
parent::__construct($values, 'breadcrumb');
}
我们将它修正为:
public function __construct($values = array()) {
parent::__construct($values, 'breadcrumb2');
}
一字之差,就让我们调试了半天,复制粘贴别人的代码的时候,经常会遇到这样的问题,要改的地方没有改过来,或者改错了。
问题4:
原来的错误消失了,新的错误出现了:
这个错误也非常严重,但是相比前面的错误,至少这个错误还能把页面完整显示出来。刚才发现Breadcrumb类定义的有问题。现在根据错误提示,“entity_id”有问题,也就是我们的bid设置的有问题,前面已经修正了一个地方了。我重读了Profile2模块里面的Profile类的定义,发现里面的代码中,包括很多属性,其中就包括pid。人家是这样定义的:
class Profile extends Entity {
/**
* The profile id.
*
* @var integer
*/
public $pid;
。。。。
当时我定义Breadcrumb类的时候,不知道这些属性的含义,另外在类的成员函数里面也没有用到这些属性,所以一股脑的把它们删除了,现在我们为Breadcrumb添加一个属性:
/**
* The breadcrumb id.
*
* @var integer
*/
public $bid;
问题5:
修改后,我们清空缓存,再次测试,原来的错误消失了,又出现了新的问题:
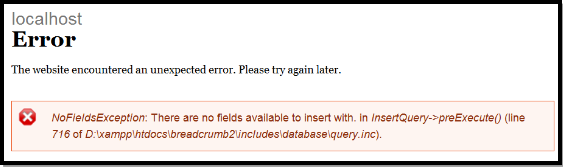
我直接打开includes\database\query.inc文件,找到716行,看源代码:
public function preExecute() {
// Confirm that the user did not try to specify an identical
// field and default field.
if (array_intersect($this->insertFields, $this->defaultFields)) {
throw new FieldsOverlapException('You may not specify the same field to have a value and a schema-default value.');
}
if (!empty($this->fromQuery)) {
// We have to assume that the used aliases match the insert fields.
// Regular fields are added to the query before expressions, maintain the
// same order for the insert fields.
// This behavior can be overridden by calling fields() manually as only the
// first call to fields() does have an effect.
$this->fields(array_merge(array_keys($this->fromQuery->getFields()), array_keys($this->fromQuery->getExpressions())));
}
// Don't execute query without fields.
if (count($this->insertFields) + count($this->defaultFields) == 0) {
throw new NoFieldsException('There are no fields available to insert with.');
}
// If no values have been added, silently ignore this query. This can happen
// if values are added conditionally, so we don't want to throw an
// exception.
if (!isset($this->insertValues[0]) && count($this->insertFields) > 0 && empty($this->fromQuery)) {
return FALSE;
}
return TRUE;
}
这里的黑体部分,就是我们出错的地方,此时我突然想到了一个问题,我们的breadcrumb数据库表,里面只有一个bid字段,并且这个字段是自增的字段。我们向数据库里面插入数据的时候,是不需要设置这个字段的,除此以外,我们没有别的字段了。我要哭了。在没有遇到这个问题以前,我是没有思考过这个问题的。我查看了多个实体类型的定义,发现主表里面,都是有属性的,即便是Field Collection里面也有一个属性field_name。现在为我们的breadcrumb数据库表,添加什么样的属性呢?最初我考虑的是created、changed,但是这两个属性对于我们来说,没有多大用处,最后我觉得,使用path,把它定义为这里的属性,不用Field模块来管理它了,当然也就不使用Field validation负责它的验证了,我们自己编写它的验证逻辑。这次改动有点多哟,好事多磨。
首先是schema里面的定义,粗体表示新增的:
'bid' => array(
'type' => 'serial',
'not null' => TRUE,
'description' => t("'Primary Key: Unique breadcrumb item ID."),
),
'path' => array(
'description' => t('URL where breadcrumb should be shown.'),
'type' => 'varchar',
'length' => 256,
'not null' => TRUE,
),
接着为类Breadcrumb,添加一个属性$path:
class Breadcrumb extends Entity {
/**
* The breadcrumb id.
*
* @var integer
*/
public $bid;
/**
* The internal path where breadcrumb should be shown.
*
* @var string
*/
public $path;
这下,我们的breadcrumb2.info.inc文件有用了:
class Breadcrumb2MetadataController extends EntityDefaultMetadataController {
public function entityPropertyInfo() {
$info = parent::entityPropertyInfo();
$properties = &$info[$this->type]['properties'];
$properties['path'] = array(
'label' => t('path'),
'description' => t('The internal path where breadcrumb should be shown.'),
'setter callback' => 'entity_property_verbatim_set',
'setter permission' => 'administer breadcrumbs',
'schema field' => 'path',
);
return $info;
}
}
当然,我们的面包屑表单里面,也需要加上这个元素:
function breadcrumb2_form($form, &$form_state, $breadcrumb) {
// Save the breadcrumb for later, in case we need it.
$form['#breadcrumb'] = $breadcrumb;
$form_state['breadcrumb'] = $breadcrumb;
$form['bid'] = array(
'#type' => 'value',
'#value' => isset($breadcrumb->bid) ? $breadcrumb->bid : NULL,
);
$form['path'] = array(
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#title' => t('Path'),
'#maxlength' => 60,
'#default_value' => !empty($breadcrumb->path) ? $breadcrumb->path : '',
'#weight' => -10,
);
做完这些修改以后,卸载breadcrumb2模块,然后重新安装,然后删除Path字段,重新测试。成功了,只不过重定向回来的时候,路径还不存在,导致了空白问题。我通过phpmyadmin检查对应的数据,基本上都正确了,就剩下一个小问题,就是path属性没有保存下来,里面一直问题。这个问题解决起来也并不复杂:
function breadcrumb2_form_submit($form, &$form_state) {
$breadcrumb = &$form_state['breadcrumb'];
$breadcrumb->bid = $form_state['values']['bid'];
$breadcrumb->path = $form_state['values']['path'];
….
粗体部分为新增的代码,这样就正常了。我是在解决这些问题的时候,更加深刻的掌握了创建一个实体类型的技术。原本打算重新写作这部分资料,后来还是觉得把过程中遇到的错误,也原原本本的呈现出来。这是Think in Drupal的一个风格,就是我们把开发中、配置中的错误也完全呈现出来,告诉大家的解决这些问题的步骤。
Drupal版本:
7.13查看面包屑实体
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
首先定义菜单项:
$items['breadcrumb/%breadcrumb2'] = array(
'title' => 'Breadcrumb',
'page callback' => 'breadcrumb2_page_view',
'page arguments' => array(1),
'access arguments' => array('administer breadcrumbs'),
'file' => 'breadcrumb2.admin.inc',
);
$items['breadcrumb/%breadcrumb2/view'] = array(
'title' => 'View',
'type' => MENU_DEFAULT_LOCAL_TASK,
'weight' => -10,
);
这里面我们使用了通配符%breadcrumb2,当我们传递过来一个bid以后,系统会自动的调用breadcrumb2_load函数,将bid转换为相应的面包屑对象。
接下来,我们看breadcrumb2_page_view的具体实现,向breadcrumb2.admin.inc里面添加以下代码:
/**
* Breadcrumb view page.
*/
function breadcrumb2_page_view($breadcrumb, $view_mode ='full'){
return $breadcrumb->view('full');
}
清除缓存,现在访问breadcrumb/1,已经可以显示出来了,但是面包屑的属性path没有显示出来。
此时有多种解决办法,一种是实现自己的控制器类BreadcrumbController,在里面实现自己的方法:
public function buildContent($entity, $view_mode = 'full', $langcode = NULL, $content = array())
另一种,是在breadcrumb2_page_view里面,我们不调用$breadcrumb->view,然后自己去构建我们想要的内容。
function breadcrumb2_page_view($breadcrumb, $view_mode = 'full'){
// return $breadcrumb->view($view_mode);
$breadcrumb->content = array();
if($view_mode = 'full'){
$breadcrumb->content['path'] = array(
'#markup' => filter_xss($breadcrumb->path),
'weight' => -5,
);
}
//Build fields content
field_attach_prepare_view('breadcrumb2', array($breadcrumb->bid => $breadcrumb), $view_mode);
entity_prepare_view('breadcrumb2', array($breadcrumb->bid => $breadcrumb));
$breadcrumb->content += field_attach_view('breadcrumb2', $breadcrumb, $view_mode);
return $breadcrumb->content;
}
这种方式是我们自己调用field的集成。当然,如果我们熟悉$breadcrumb->view返回的数组结构的话,也可以这样编写代码:
$build = $breadcrumb->view($view_mode);
if($view_mode = 'full'){
$build['breadcrumb2'][$breadcrumb->bid]['path'] = array(
'#markup' => filter_xss($breadcrumb->path),
'weight' => -5,
);
}
return $build;
第三种办法,就是自己实现hook_ breadcrumb2_view这个钩子,这个钩子是从哪里定义的?这是Entity API模块帮助我们定义,只需要自己去实现即可,在module文件中添加以下代码,效果是一样的:
/**
* Implement hook_breadcrumb2_view().
*/
function breadcrumb2_breadcrumb2_view($breadcrumb, $view_mode, $langcode){
if($view_mode = 'full'){
$breadcrumb->content['path'] = array(
'#markup' => filter_xss($entity->path),
'weight' => -5,
);
}
}
从这里面,我们可以看到Entity API帮助我们做了很多工作,省了不少事。
Drupal版本:
7.14 编辑面包屑实体
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
菜单项代码:
$items['breadcrumb/%breadcrumb2/edit'] = array(
'page callback' => 'breadcrumb2_page_edit',
'page arguments' => array(1),
'access arguments' => array('administer breadcrumbs'),
'weight' => 0,
'title' => 'Edit',
'type' => MENU_LOCAL_TASK,
'context' => MENU_CONTEXT_PAGE | MENU_CONTEXT_INLINE,
'file' => 'breadcrumb2.admin.inc',
);
这里在菜单项里面,用到了'context',它的含义可以参看第一集。接着我们向breadcrumb2.admin.inc添加breadcrumb2_page_edit函数:
/**
* Breadcrumb edit page.
*/
function breadcrumb2_page_edit($breadcrumb){
return drupal_get_form('breadcrumb2_form', $breadcrumb);
}
由于我们在前面创建面包屑的时候,编写breadcrumb2_form表单时,同时考虑了编辑时会用到,所以我们这里的代码就简洁了很多。将添加表单、编辑表单合二为一,这是一个好习惯。
Drupal版本:
7.15 删除面包屑实体
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
首先我们实现删除按钮的提交处理函数breadcrumb2_form_submit_delete:
/**
* Breadcrumb form submit handler for the delete button.
*/
function breadcrumb2_form_submit_delete($form, &$form_state) {
$breadcrumb = $form_state['breadcrumb'];
$form_state['redirect'] = 'breadcrumb/' . $breadcrumb->bid . '/delete';
}
在这里,当删除一个面包屑时,我们直接将它重定向到了对应的删除页面。对应路径的菜单项是这样定义的:
$items['breadcrumb/%breadcrumb2/delete'] = array(
'page callback' => 'drupal_get_form',
'page arguments' => array('breadcrumb2_delete_confirm_form', 1),
'access arguments' => array('administer breadcrumbs'),
'weight' => 1,
'title' => 'Delete',
'type' => MENU_LOCAL_TASK,
'context' => MENU_CONTEXT_INLINE,
'file' => 'breadcrumb2.admin.inc',
);
breadcrumb2_delete_confirm_form是一个确认表单,我们把它的定义添加到breadcrumb2.admin.inc里面:
/**
* Confirm form for deleting a profile.
*/
function breadcrumb2_delete_confirm_form($form, &$form_state, $breadcrumb) {
$form_state += array('breadcrumb' => $breadcrumb);
$confirm_question = t('Are you sure you want to delete breadcrumb for path %path?', array('%path' => $breadcrumb->path));
return confirm_form($form, $confirm_question, 'breadcrumb/' . $breadcrumb->bid);
}
确认表单,采用了confirm_form,让Drupal系统来生成这个表单。最后我们来看一下,确认表单提交后的代码:
function breadcrumb2_delete_confirm_form_submit($form, &$form_state) {
$breadcrumb = $form_state['breadcrumb'];
$breadcrumb->delete();
drupal_set_message(t('Deleted breadcrumb for path %path.', array('%path' => $breadcrumb->path)));
$form_state['redirect'] = 'admin/structure/breadcrumbs';
}
这里面的代码,主要借鉴了Profile2里面的profile2_page.inc文件里面的代码。
Drupal版本:
7.16 安装时为实体创建字段
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们这里是手动的创建Breadcrumb link字段,我们希望在安装这个Breadcrumb2模块的时候,自动的帮我们创建这个字段。这个字段,对我们来说是必须的。首先,我们把现有的字段的信息导出来。这里我们使用Features模块。
这是Features导出来的代码:
/**
* Implements hook_field_default_fields().
*/
function breadcrumb_link_field_default_fields() {
$fields = array();
// Exported field: 'breadcrumb2-breadcrumb2-field_breadcrumb_link'
$fields['breadcrumb2-breadcrumb2-field_breadcrumb_link'] = array(
'field_config' => array(
'active' => '1',
'cardinality' => '-1',
'deleted' => '0',
'entity_types' => array(),
'field_name' => 'field_breadcrumb_link',
'foreign keys' => array(),
'indexes' => array(),
'module' => 'link',
'settings' => array(
'attributes' => array(
'class' => '',
'rel' => '',
'target' => 'default',
),
'display' => array(
'url_cutoff' => 80,
),
'enable_tokens' => 1,
'title' => 'optional',
'title_maxlength' => 128,
'title_value' => '',
'url' => 0,
),
'translatable' => '0',
'type' => 'link_field',
),
'field_instance' => array(
'bundle' => 'breadcrumb2',
'default_value' => NULL,
'deleted' => '0',
'description' => '',
'display' => array(
'default' => array(
'label' => 'above',
'module' => 'link',
'settings' => array(),
'type' => 'link_default',
'weight' => 1,
),
),
'entity_type' => 'breadcrumb2',
'field_name' => 'field_breadcrumb_link',
'label' => 'Breadcrumb Link',
'required' => 0,
'settings' => array(
'attributes' => array(
'class' => '',
'configurable_title' => 0,
'rel' => '',
'target' => 'default',
'title' => '',
),
'display' => array(
'url_cutoff' => '80',
),
'enable_tokens' => 1,
'title' => 'required',
'title_maxlength' => '128',
'title_value' => '',
'url' => 'optional',
'user_register_form' => FALSE,
'validate_url' => 1,
),
'widget' => array(
'active' => 0,
'module' => 'link',
'settings' => array(),
'type' => 'link_field',
'weight' => '2',
),
),
);
// Translatables
// Included for use with string extractors like potx.
t('Breadcrumb Link');
return $fields;
}
我把它改造了一下,放到了install文件里面了,我们这里并没有打算依赖于Features模块:
/**
* Implements hook_install().
*/
function breadcrumb2_install() {
// Add or remove the link field, as needed.
$field = field_info_field('link');
if (empty($field)) {
$field = array(
'cardinality' => '-1',
'entity_types' => array('breadcrumb2'),
'field_name' => 'link',
'module' => 'link',
'type' => 'link_field',
);
$field = field_create_field($field);
}
$instance = field_info_instance('breadcrumb2', 'link', 'breadcrumb2');
if (empty($instance)) {
$instance = array(
'bundle' => 'breadcrumb2',
'default_value' => NULL,
'deleted' => '0',
'description' => '',
'display' => array(
'default' => array(
'label' => 'above',
'module' => 'link',
'settings' => array(),
'type' => 'link_default',
'weight' => 1,
),
),
'entity_type' => 'breadcrumb2',
'field_name' => 'link',
'label' => 'Breadcrumb Link',
'required' => 0,
'settings' => array(
'attributes' => array(
'class' => '',
'configurable_title' => 0,
'rel' => '',
'target' => 'default',
'title' => '',
),
'display' => array(
'url_cutoff' => '80',
),
'enable_tokens' => 1,
'title' => 'required',
'title_maxlength' => '128',
'title_value' => '',
'url' => 'optional',
'user_register_form' => FALSE,
'validate_url' => 1,
),
'widget' => array(
'active' => 0,
'module' => 'link',
'settings' => array(),
'type' => 'link_field',
'weight' => '2',
),
);
$instance = field_create_instance($instance);
}
}
在卸载我们的模块时,我们还需要负责将其删除:
/**
* Implements hook_uninstall().
*/
function breadcrumb2_uninstall() {
$instance = field_info_instance('breadcrumb2', 'link', 'breadcrumb2');
if (!empty($instance)) {
field_delete_instance($instance);
}
$field = field_info_field('link');
if ($field) {
field_delete_field('link');
}
}
注意这里面的field_info_field、field_create_field、field_info_instance、field_create_instance、field_delete_instance、field_delete_field等Drupal API函数的用法。它们用来获取字段信息、创建一个字段、获取字段实例信息、创建一个字段实例、删除一个字段实例、删除一个字段。
我刚开始的时候,这样写的代码:
field_delete_field($field);
结果在卸载模块的时候,总是报错,卸载不了。后来才修正过来。所以用的时候要小心。要明白这个函数里面各个参数的具体含义。
Drupal版本:
7.17 面包屑本身功能实现
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们这个模块,是用来设置页面上面的面包屑的,开发了这么多,我们看看如果通过我们的面包屑实体来设置面包屑。向module文件添加以下代码:
/**
* Implements hook_page_alter().
*/
function breadcrumb2_page_alter() {
// See if current page has path breadcrumbs.
$breadcrumbs = drupal_get_breadcrumb();
$current_path = current_path();
$breadcrumb2 = breadcrumb2_load_by_path($current_path);
if(empty($breadcrumb2)){
return;
}
//$breadcrumb2 = breadcrumb2_load(1);
$wrapper = entity_metadata_wrapper('breadcrumb2', $breadcrumb2);
$breadcrumb_links = $wrapper->link->value();
foreach($breadcrumb_links as $breadcrumb_link){
$breadcrumbs[]= l($breadcrumb_link['title'], $breadcrumb_link['url']);
}
//print debug($breadcrumb_links);
// Set breadcrumbs for current page if it exists.
if ($breadcrumbs) {
drupal_set_breadcrumb($breadcrumbs);
}
}
这里面我们实现了hook_page_alter钩子,这个方式借鉴于path_breadcrumb模块,当然,我们也可以通过hook_preprocess_page来设置, crumbs模块里面有这种方式的实现。我们来看看这个钩子函数里面的代码,首先,我们根据当前路径,获取到面包屑实体$breadcrumb2;这里面我们对$breadcrumb2使用entity_metadata_wrapper做了封装,这样我们就可以方便的读取到实体里面字段link的数组了,这样做的好处是,不用考虑语言问题;之后对$breadcrumb_links数组进行循环,将里面的链接追加到当前面包屑数组$breadcrumbs里面;最后使用drupal_set_breadcrumb设置面包屑。
接下来,来看一下函数breadcrumb2_load_by_path的实现代码:
/**
* Fetch a breadcrumb object.
*
* @param $path
* Internal path.
* @return
* A fully-loaded $breadcrumb object or FALSE if it cannot be loaded.
*
* @see breadcrumb2_load_multiple()
*/
function breadcrumb2_load_by_path($path) {
$breadcrumbs = breadcrumb2_load_multiple(FALSE, array('path' => $path));
return reset($breadcrumbs);
}
我们直接将其委托给了breadcrumb2_load_multiple,把array('path' => $path)作为条件参数传递了过去。如果返回了面包屑对象数组,我们就使用reset将数组中的第一个对象返回。这里的逻辑非常简单,和breadcrumb2_load函数类似。不过越是简单的东西,有时候越难理解。我原来的想法是这样的,使用EntityFieldQuery,把我们的$path作为属性参数传递给它,这样EntityFieldQuery将会读取来一个包含bids的数组,我们把bids数组传递给breadcrumb2_load_multiple,获得一组面包屑对象,然后再使用reset获取第一个对象元素。
Entity API帮我们做了这些工作,为了更好的理解,我们反向追踪一下代码。

通过阅读里面的代码,我们最终找到了,SQL语句是在DrupalDefaultEntityController里面的buildQuery方法中动态构建的。有兴趣的可以看一下里面的代码。
到这里我们的面包屑实体类型就创建完毕了。当然,模块还没有写完。我们接着会写Views的集成、Rules的集成。只有当集成了Rules以后,我们这种构建面包屑的方式,才能
Drupal版本:
7.2 为实体定义Schema
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
和开发普通的模块一样,当需要存储数据的时候,我们需要定义自己的数据库表,这个时候,就需要定义Schema了。这个我们以前也讲过了,来看这里的定义。首先创建breadcrumb2.install文件,在里面输入以下内容:
<?php
/**
* @file
* Install, update and uninstall functions for the breadcrumb2 module.
*/
/**
* Implements hook_schema().
*/
function breadcrumb2_schema() {
$schema['breadcrumb'] = array(
'description' => 'Stores breadcrumb items.',
'fields' => array(
'bid' => array(
'type' => 'serial',
'not null' => TRUE,
'description' => t("'Primary Key: Unique breadcrumb item ID."),
),
),
'primary key' => array('bid'),
);
return $schema;
}
最上面的文件的描述说明,那段文字是直接从profile2.install里面复制过来的,下面的breadcrumb2_schema也是从那边复制过来的,只不过我们根据自己的需要做了修改。面包屑,这个实体比较简单,本来我想在这里定义一个属性path的,但是一想,自己需要为它创建一个表单元素,负责它的编辑、验证、存储,感觉有点麻烦,所以直接将它交给Field系统了。所以数据库表breadcrumb的结构非常简单,就一个bid主键,用来关联字段的,其它什么属性也没有定义。简单就好。
我们采用这样的策略,首先,定义好实体,然后向实体上面添加两个字段path、link,之后将这两个字段的定义使用Features导出来,然后把里面的定义代码复制到我们的模块里面,这样我们在安装的时候,就直接为我们的面包屑实体创建好字段了。一步一步来。
Drupal版本:
7.3 实现hook_entity_info
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
接下来,我们创建breadcrumb2.module文件,首先输入以下代码:
<?php
/**
* @file
* Support for configurable breadcrumbs.
*/
接着,实现hook_entity_info()。
/**
* Implement hook_entity_info().
*/
function breadcrumb2_entity_info() {
$return = array(
'breadcrumb2' => array(
'label' => t('Breadcrumb'),
'plural label' => t('Breadcrumbs'),
'description' => t('Breadcrumb2 entity breadcrumbs.'),
'entity class' => 'Breadcrumb',
'controller class' => 'EntityAPIController',
'base table' => 'breadcrumb',
'fieldable' => TRUE,
'view modes' => array(
'full' => array(
'label' => t('Breadcrumb'),
'custom settings' => FALSE,
),
),
'entity keys' => array(
'id' => 'pid',
),
'bundles' => array(
'breadcrumb2' => array(
'label' => t('Breadcrumb'),
'admin' => array(
'path' => 'admin/structure/breadcrumbs',
'access arguments' => array('administer breadcrumbs'),
),
),
),
'bundle keys' => array(
'bundle' => 'type',
),
'uri callback' => 'entity_class_uri',
'access callback' => 'breadcrumb2_access',
'module' => 'breadcrumb2',
'metadata controller class' => 'Breadcrumb2MetadataController'
),
);
return $return;
}
首先,这个钩子的实现,我们主要参考了profile2_entity_info的实现,这里是以它为基础做的修改。其次,由于我们这里只有一个bundle,并且不允许创建其它的bundle,这个和user实体非常类似,所以中间的部分代码,我们借鉴的是user_entity_info的实现,我们来看一下user模块的实现:
function user_entity_info() {
$return = array(
'user' => array(
'label' => t('User'),
'controller class' => 'UserController',
'base table' => 'users',
'uri callback' => 'user_uri',
'label callback' => 'format_username',
'fieldable' => TRUE,
// $user->language is only the preferred user language for the user
// interface textual elements. As it is not necessarily related to the
// language assigned to fields, we do not define it as the entity language
// key.
'entity keys' => array(
'id' => 'uid',
),
'bundles' => array(
'user' => array(
'label' => t('User'),
'admin' => array(
'path' => 'admin/config/people/accounts',
'access arguments' => array('administer users'),
),
),
),
'view modes' => array(
'full' => array(
'label' => t('User account'),
'custom settings' => FALSE,
),
),
),
);
return $return;
}
我们的'entity keys'、'bundles'、'view modes',都是从user_entity_info借鉴过来的。所谓借鉴,就是将它们的代码复制过来,然后改成我们自己的。比葫芦画瓢。比如'entity keys',最初这个是从profile2中借鉴过来的,profile2_entity_info中这样定义的:
'entity keys' => array(
'id' => 'pid',
'bundle' => 'type',
'label' => 'label',
),
我们知道,pid是profile里面的主键,我们将它修改为bid,就成了最初的样子:
'entity keys' => array(
'id' => 'bid',
'bundle' => 'type',
'label' => 'label',
),
然后再借鉴一下user里面的实现,这个时候,我们会发现里面的'bundle'、'label'没有什么用,把它们删除,就成了现在的样子:
'entity keys' => array(
'id' => 'pid',
),
Drupal里面的很多钩子,尤其是这种带有info后缀的钩子,里面通常是一个大的数组,遇到这样的钩子,我们学习的路径,最好是找个类似的实现作为参考,当然我们还需要阅读这个钩子的文档,弄清楚里面的键值的具体含义,不过大部分键的含义,从字面上很容易理解出来,比如这里的'label'、'plural label'、'description'、'entity class'、'controller class'、'base table'、'fieldable'等。
Drupal版本:
7.4 实现Hook_menu
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们在hook_entity_info里面,有这样的设置“'path' => 'admin/structure/breadcrumbs'”,
这里所用的路径,我们需要在hook_menu里面定义一下,现在我们就来实现这个路径。向module文件中添加以下代码:
/**
* Implements hook_menu().
*/
function breadcrumb2_menu() {
$items['admin/structure/breadcrumbs'] = array(
'title' => 'Breadcrumbs',
'description' => 'Manage breadcrumbs.',
'page callback' => 'breadcrumb2_overview_breadcrumbs',
'access arguments' => array('administer breadcrumbs'),
'file' => 'breadcrumb2.admin.inc',
);
$items['admin/structure/breadcrumbs/list'] = array(
'title' => 'List',
'type' => MENU_DEFAULT_LOCAL_TASK,
'weight' => -10,
);
}
注意,我们必须把admin/structure/breadcrumbs/list指定为MENU_DEFAULT_LOCAL_TASK,这样Field模块可以在admin/structure/breadcrumbs路径后面添加两个子标签,管理字段、管理显示。
接着创建breadcrumb2.admin.inc文件,向里面添加我们的回调函数breadcrumb2_overview_breadcrumbs:
<?php
/**
* @file
* Breadcrumb administration and module settings UI.
*
*/
/**
* Displays the breadcrumb admin overview page.
*/
function breadcrumb2_overview_breadcrumbs(){
$build['#markup'] = t('Breadcrumb2 overview breadcrumbs');
return $build;
}
这里面还没有逻辑代码。我们只是想快速的实现一个骨架,然后再逐步的完善里面具体的细节。
Drupal版本:
7.5 权限与访问控制
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
在我们的菜单项里面,用到了权限'administer breadcrumbs',现在就让我们定义这个权限,向module文件中添加以下代码:
/**
* Implements hook_permission().
*/
function breadcrumb2_permission() {
$permissions = array(
'administer breadcrumbs' => array(
'title' => t('Administer breadcrumbs'),
'description' => t('Edit and view all entity breadcrumbs.'),
),
);
return $permissions;
}
面包屑也有增删查改,但是这些工作都是由管理员来做的,所以我们这里比较省事,就定义了一个'administer breadcrumbs'权限,其它的都省去了。
在hook_entity_info里面,有这样的定义'access callback' => 'breadcrumb2_access',这里的breadcrumb2_access,就是一个访问控制回调函数,来看一下我们的实现:
/**
* Determines whether the given user has access to a breadcrumb.
*
* @param $op
* The operation being performed. One of 'view', 'update', 'create', 'delete'
* or just 'edit' (being the same as 'create' or 'update').
* @param $breadcrumb
* Optionally a breadcrumb to check access for. If nothing is
* given, access for all breadcrumbs is determined.
* @param $account
* The user to check for. Leave it to NULL to check for the global user.
* @return boolean
* Whether access is allowed or not.
*/
function breadcrumb2_access($op, $breadcrumb = NULL, $account = NULL) {
if (user_access('administer breadcrumbs', $account)) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
对于比较复杂的实体,比如profile2,这个访问回调里面还会定义一个新的钩子hook_profile2_access。
function profile2_access($op, $profile = NULL, $account = NULL) {
if (user_access('administer profiles', $account)) {
return TRUE;
}
if ($op == 'create' || $op == 'update') {
$op = 'edit';
}
// Allow modules to grant / deny access.
$access = module_invoke_all('profile2_access', $op, $profile, $account);
// Only grant access if at least one module granted access and no one denied
// access.
if (in_array(FALSE, $access, TRUE)) {
return FALSE;
}
elseif (in_array(TRUE, $access, TRUE)) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
在node_access里面,也定义了类似的钩子:
$access = module_invoke_all('node_access', $node, $op, $account);
当然,我们这里不需要定义一个hook_breadcrumb2_access,所以我们的就比较简单。
Drupal版本:
7.6 加载、删除、创建、保存实体
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
对于定义的实体类型,我们最好为其实现增删改查等API函数,方便别处调用:
{entity_type}_load(),
{entity_type}_create(),
{entity_type}_save(),
{entity_type}_delete_multiple(),
Entity API模块,为我们提供了entity_create()、 entity_save()、 entity_delete()等函数,直接使用Entity API里面的即可,我们还有必要定义自己的么?最好还是定义一下,也就是有这个必要。我们来看看我们的实现:
/**
* Fetch a breadcrumb object.
*
* @param $bid
* Integer specifying the breadcrumb id.
* @param $reset
* A boolean indicating that the internal cache should be reset.
* @return
* A fully-loaded $breadcrumb object or FALSE if it cannot be loaded.
*
* @see breadcrumb2_load_multiple()
*/
function breadcrumb2_load($bid, $reset = FALSE) {
$breadcrumbs = breadcrumb2_load_multiple(array($bid), array(), $reset);
return reset($breadcrumbs);
}
/**
* Load multiple breadcrumbs based on certain conditions.
*
* @param $bids
* An array of breadcrumb IDs.
* @param $conditions
* An array of conditions to match against the {breadcrumb} table.
* @param $reset
* A boolean indicating that the internal cache should be reset.
* @return
* An array of breadcrumb objects, indexed by bid.
*
* @see entity_load()
* @see breadcrumb2_load()
*/
function breadcrumb2_load_multiple($bids = array(), $conditions = array(), $reset = FALSE) {
return entity_load('breadcrumb2', $bids, $conditions, $reset);
}
/**
* Deletes a breadcrumb.
*/
function breadcrumb2_delete(Breadcrumb $breadcrumb) {
$breadcrumb->delete();
}
/**
* Delete multiple breadcrumbs.
*
* @param $bids
* An array of breadcrumb IDs.
*/
function breadcrumb2_delete_multiple(array $bids) {
entity_get_controller('breadcrumb2')->delete($bids);
}
/**
* Create a breadcrumb object.
*/
function breadcrumb2_create($values = array()) {
return new Breadcrumb($values);
}
/**
* Saves a breadcrumb to the database.
*
* @param $breadcrumb
* The breadcrumb object.
*/
function breadcrumb2_save(Breadcrumb $breadcrumb) {
return $breadcrumb->save();
}
这都是模式化的代码,对应的实现,可以参考profile2,也可以参考model模块。
Drupal版本:
7.7 定义实体类
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们在breadcrumb2_entity_info里面,将'entity class'指定为了Breadcrumb,现在我们来看看这个类的定义。向breadcrumb2.module里面添加以下代码:
/**
* The class used for breadcrumb entities
*/
class Breadcrumb extends Entity {
public function __construct($values = array()) {
parent::__construct($values, 'breadcrumb');
}
protected function defaultLabel() {
return $this->path;
}
protected function defaultUri() {
return array('path' => 'breadcrumb/' . $this->bid);
}
}
类似的代码可以参看model里面的Model类的实现。
我们将'controller class'设置为了EntityAPIController,当然,我们也可以有自己的实现,比如将其设置为BreadcrumbController。此时需要定义这个控制器类,我们向module文件追加以下代码:
/**
* The Controller for Breadcrumb entities
*/
class BreadcrumbController extends EntityAPIController {
public function __construct($entityType) {
parent::__construct($entityType);
}
/**
* Create a breadcrumb - we first set up the values that are specific
* to our breadcrumb schema but then also go through the EntityAPIController
* function.
*
* @param $type
* The machine-readable type of the breadcrumb.
*
* @return
* A breadcrumb object with all default fields initialized.
*/
public function create(array $values = array()) {
// Add values that are specific to our Breadcrumb
$values += array(
'bid' => '',
);
$breadcrumb = parent::create($values);
return $breadcrumb;
}
}
这里也是模仿的model模块的实现。
Drupal版本:
7.8 元数据控制器类
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们将'metadata controller class'设置为了Breadcrumb2MetadataController,对于这个类型,我们将它放到了breadcrumb2.info.inc文件中了。来看一下它的代码:
<?php
/**
* @file
* Provides Entity metadata integration.
*/
/**
* Extend the defaults.
*/
class Breadcrumb2MetadataController extends EntityDefaultMetadataController {
public function entityPropertyInfo() {
$info = parent::entityPropertyInfo();
$properties = &$info[$this->type]['properties'];
return $info;
}
}
我们这里面,这个类是空类,里面其实没有自己的实现。我们是模仿profile2的,它的这个元数据控制器类,是这样定义的:
class Profile2MetadataController extends EntityDefaultMetadataController {
public function entityPropertyInfo() {
$info = parent::entityPropertyInfo();
$properties = &$info[$this->type]['properties'];
$properties['label'] = array(
'label' => t('Label'),
'description' => t('The profile label.'),
'setter callback' => 'entity_property_verbatim_set',
'setter permission' => 'administer profiles',
'schema field' => 'label',
);
…
return $info;
}
}
/**
* Implements hook_entity_property_info_alter().
*/
function profile2_entity_property_info_alter(&$info) {
…
}
我们的面包屑里面,除了bid,不包含其它属性,同时只有一个bundle,我们这里可能就不需要定义这个元数据控制器类,只需要使用Entity API提供的默认的EntityDefaultMetadataController即可。
另外需要注意的是,在这个info.inc文件里面可以定义实现钩子hook_entity_property_info_alter。如果这个钩子实现可以放在这里的话,那么也可以在这里实现hook_entity_property_info,这是我的猜测。这样做的目的也是为了减小module文件的大小。
Drupal版本:
7.9 调试代码
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
一切工作准备就绪,让我们启用Breadcrumb2模块,我们需要预先安装好它所依赖的模块。都准备好了。启用好模块以后,没有报错,接着我们访问admin/structure,在这里我们并没有找到我们的面包屑:

而管理字段、管理显示两个标签却显示了出来,点击这两个标签,发现它们的路径分别为admin/structure/breadcrumbs/fields,admin/structure/breadcrumbs/display。功能和我们在其它地方看到的一样。admin/structure/breadcrumbs哪里去了?
我们回过头来检查代码,发现我们在breadcrumb2_menu少写下面一句代码:
return $items;
一个很低级的错误。我们把它补上。我最初开发的时候,除了这个问题,还遇到了找不到Breadcrumb2MetadataController类的问题。因为我没有创建breadcrumb2.info.inc文件,也没有添加Breadcrumb2MetadataController的实现。我是在发现admin/structure/breadcrumbs不存在这个问题以后,清空缓存后,整个网站无法访问了,并且提示Breadcrumb2MetadataController不存在。这个时候,我才添加的breadcrumb2.info.inc文件。
现在清除缓存,admin/structure/breadcrumbs显示出来了:

Drupal版本:
8 EntityFieldQuery
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
在没有使用EntitiFieldQuery之前,我一直都是采用db_select的形式,这个我们在前面已经讲过了。我们先来看一个实际的例子,这段代码主要是我写的:
<?php
/**
* @file
* Field validation unique validator.
*
*/
$plugin = array(
'label' => t('Unique values'),
'description' => t('Verifies that all values are unique in current entity or bundle.'),
'handler' => array(
'class' => 'field_validation_unique_validator',
),
);
class field_validation_unique_validator extends field_validation_validator {
/**
* Validate field.
*/
public function validate() {
$flag = TRUE;
$scope = $this->rule->settings['data'];
$count = 0;
foreach ($this->items as $delta1 => $item1) {
if ($this->delta != $delta1) {
if ($this->value == $item1[$this->rule->col]) {
$flag = FALSE;
break;
}
}
}
if ($flag) {
$query = new EntityFieldQuery();
if ($scope == 'global') {
}
elseif ($scope == 'entity') {
$query->entityCondition('entity_type', $this->rule->entity_type);
}
elseif ($scope == 'bundle') {
$query->entityCondition('entity_type', $this->rule->entity_type);
$query->entityCondition('bundle', $this->rule->bundle);
}
list($id, $vid, $bundle) = entity_extract_ids($this->rule->entity_type, $this->entity);
if ($this->rule->entity_type == 'user' && arg(0) =='user' && arg(2) =='edit' && empty($id)) {
$id = arg(1);
}
if ($this->rule->entity_type == 'field_collection_item' && arg(0) == 'field-collection' && arg(3) =='edit' && empty($id)) {
$id = arg(2);
}
if ($this->rule->entity_type == 'profile2' && empty($id)) {
$arg_index = 1;
if (module_exists('profile2_page')) {
$profile_type = profile2_type_load($this->entity->type);
$path = profile2_page_get_base_path($profile_type);
$arg_index = count(explode('/', $path));
}
$uid = arg($arg_index);
if (arg($arg_index + 1) == 'edit' && is_numeric($uid) && $account = user_load($uid)) {
if ($profile = profile2_load_by_user($account, $this->entity->type)) {
$id = $profile->pid;
}
}
}
if (!empty($id)) {
$query->entityCondition('entity_id', $id, '!=');
}
//Always bypass all access checkings.
$query->addMetaData('account', user_load(1));
$query->fieldCondition($this->rule->field_name, $this->rule->col, $this->value);
// Store a copy of our matched entities for our use in tokens later.
$matched_entities = $query->execute();
$count = $query
->count()
->execute();
if ($count) {
$flag = FALSE;
}
}
if (!$flag) {
$token = array(
'[count]' => $count,
);
// Find the first entity that failed this unique condition so we can
// add a token referencing it. First, we have some special handling for
// field collection entities so we can find the entity title of
// whatever the specific field is connected to.
$entity_types = array_keys($matched_entities);
$entity_type = reset($entity_types);
$matched_entity = reset($matched_entities);
$first_match = reset($matched_entity);
$entity_info = entity_get_info($entity_type);
$entity_key_id = $entity_info['entity keys']['id'];
$entitys = entity_load($entity_type, array($first_match->{$entity_key_id}));
$entity = reset($entitys);
if ($entity_type == 'field_collection_item') {
$host_type = $entity->hostEntityType();
$host_entity = $entity->hostEntity();
$label = entity_label($host_type, $host_entity);
$uri = entity_uri($host_type, $host_entity);
}
else {
$label = entity_label($entity_type, $entity);
$uri = entity_uri($entity_type, $entity);
}
$token['[existing-entity-label]'] = $label;
$token['[existing-entity-link]'] = l($label, $uri['path'], $uri['options']);
$this->set_error($token);
}
}
/**
* Provide settings option
*/
function settings_form(&$form, &$form_state) {
$default_settings = $this->get_default_settings($form, $form_state);
//print debug($default_settings);
$form['settings']['data'] = array(
'#title' => t('Scope of unique'),
'#description' => t("Specify the scope of unique values, support: global, entity, bundle."),
'#type' => 'select',
'#options' => array(
'global' => t('Global'),
'entity' => t('Entity'),
'bundle' => t('Bundle'),
),
'#default_value' => isset($default_settings['data']) ? $default_settings['data'] : '',
);
parent::settings_form($form, $form_state);
}
/**
* Provide token help info for error message.
*/
public function token_help() {
$token_help = parent::token_help();
$token_help += array(
'[count]' => t('Count of duplicate'),
'[existing-entity-label]' => t('The label of the first entity that contains matching data.'),
'[existing-entity-link]' => t('A link to the first entity that contains matching data.'),
);
return $token_help;
}
}
这里面涵盖了EntitiFieldQuery的常见用法,首先,我们使用下面的语句,初始化查询语句:
$query = new EntityFieldQuery();
Drupal版本:
8.1条件语句
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
接着,可以为它添加一些条件语句,比如使用entityCondition添加实体本身相关的条件语句:
$query->entityCondition('entity_type', $this->rule->entity_type);
$query->entityCondition('bundle', $this->rule->bundle);
$query->entityCondition('entity_id', $id, '!=');
注意,这里面entity_id,也属于entityCondition的范畴。函数的结构定义是这样的:
public function entityCondition($name, $value, $operator = NULL)
$name,这里的允许值有'entity_type', 'bundle', 'revision_id' 或'entity_id',注意有些实体,比如评论、分类术语,它们不能使用'bundle'。$value就是当前值,$operator是操作符,默认使用“=”,可用的操作符有'=', '<>', '>', '>=', '<', '<=', 'STARTS_WITH', 'CONTAINS', 'IN', 'NOT IN', 'BETWEEN'。注意,后面三个操作符都是作用于数组的。
也可以使用fieldCondition添加字段相关的条件语句:
$query->fieldCondition($this->rule->field_name, $this->rule->col, $this->value);
这是我们这个例子里面用到的。fieldCondition的结构定义是这样的:
public function fieldCondition($field, $column = NULL, $value = NULL, $operator = NULL, $delta_group = NULL, $language_group = NULL)
这里的参数比较多,常用的就是前面四个,后面的我从来没有用过。
在property_validation模块里面的property_validation_unique_validator,还有属性相关的条件语句:
$query->propertyCondition($this->rule->property_name, $this->value) ;
这个成员函数的结构是这样的:
public function propertyCondition($column, $value, $operator = NULL)
$column就是属性名字,$value就是当前值, $operator就是操作符。
获取查询的结果
加了这么多条件语句以后,使用execute()方法就可以获取查询的结果:
$matched_entities = $query->execute();
当然,我们需要注意,返回的结果的数据结构,通常对于返回的结果,进行这样的处理:
foreach ($matched_entities as $entity_type => $entities) {
foreach ($entities as $entity_id => $entity) {
// 这里进行操作
}
}
如果我们这里已经知道了实体的类型,则可以这样处理:
$result = $query->execute();
$entities = entity_load($my_type, array_keys($result[$my_type]));
由于EntitiFieldQuery里面获取到的实体对象,仅仅是一个壳子,所以,我们还需要使用entity_load来加载它。我们在例子中,为了获取到第一个匹配到的实体,这样处理的:
$entity_types = array_keys($matched_entities);
$entity_type = reset($entity_types);
$matched_entity = reset($matched_entities);
$first_match = reset($matched_entity);
$entity_info = entity_get_info($entity_type);
$entity_key_id = $entity_info['entity keys']['id'];
$entitys = entity_load($entity_type, array($first_match->{$entity_key_id}));
$entity = reset($entitys);
这里使用多次使用reset,用来获取一个数组里面的第一个元素,注意,不能够将array_keys($matched_entities)直接传递给reset,如果这样做的话,会提示有语法问题,但是结果仍然是正确的。
使用Count()获取结果记录总数
我们这里的例子是这样的:
$count = $query->count()->execute();
另外,这里面需要说明的是,这些成员函数之间,是可以链式调用的。
Drupal版本:
9 使用addMetaData向查询添加元数据信息
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
我们这里要实现的是,查询不受权限的影响,这里通过addMetaData方法,添加一个用户1,这样就可以以用户1的身份来执行查询语句了,这样的好处就是可以跳过所有的权限检查。这是addMetaData的一个用法。
$query->addMetaData('account', user_load(1));
实际当中其它常用的方法
排序方法,有三个可用,分别为:
public function entityOrderBy($name, $direction = 'ASC') {}
public function fieldOrderBy($field, $column, $direction = 'ASC') {}
public function propertyOrderBy($column, $direction = 'ASC') {}
排序的方向默认是按照升序'ASC'进行的,如果需要降序的话,则可以使用"DESC"。
范围查询,可以使用:
public function range($start = NULL, $length = NULL) {}
为查询启用分页功能,则可以使用:
public function pager($limit = 10, $element = NULL) {}
Drupal版本:
6完善的API函数
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
这个模块提供了更多的API函数,比如entity_create()、 entity_save()、 entity_delete()、 entity_view()、 entity_access(),这些函数可以用来方便的创建、保存、删除、查看实体,最后一个entity_access用来控制访问权限的。除了这几个以外,还有entity_id()、 entity_export()、 entity_import()、entity_get_property_info()。entity_id()是用来获取id的,entity_export负责导出,entity_import负责导入;entity_get_property_info是用来做什么的?它是用来获取实体上面的属性信息的,注意这里的属性,和Drupal核心里面的属性是不一样的概念,在Drupal7核心里面,属性是属性,字段是字段,而在Entity API模块里面,属性、字段都是属性。
Drupal版本:
6.1 hook_entity_property_info
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
Entity API模块定义了一个新的钩子,hook_entity_property_info(),通过这个钩子函数,就可以定义实体包含哪些属性信息了,这个信息里面还包括,属性的数据类型、获取、设置属性的回调函数。注意,很多常用的模块,都用到了这里定义的属性,比如Rules模块。而前面的entity_get_property_info,则是用来获取hook_entity_property_info()里面的定义信息的。这个钩子函数比较抽象,我们可以看一个例子,在sites\all\modules\entity\modules下面可以找到,Drupal核心中各个子系统的钩子实现。下面这个是用户系统的实现:
/**
* Implements hook_entity_property_info() on top of user module.
*
* @see entity_entity_property_info()
*/
function entity_metadata_user_entity_property_info() {
$info = array();
// Add meta-data about the user properties.
$properties = &$info['user']['properties'];
$properties['uid'] = array(
'label' => t("User ID"),
'type' => 'integer',
'description' => t("The unique ID of the user account."),
'schema field' => 'uid',
);
$properties['name'] = array(
'label' => t("Name"),
'description' => t("The login name of the user account."),
'getter callback' => 'entity_metadata_user_get_properties',
'setter callback' => 'entity_property_verbatim_set',
'sanitize' => 'filter_xss',
'required' => TRUE,
'access callback' => 'entity_metadata_user_properties_access',
'schema field' => 'name',
);
…
下面的这段则是节点系统的实现:
…
$properties['created'] = array(
'label' => t("Date created"),
'type' => 'date',
'description' => t("The date the node was posted."),
'setter callback' => 'entity_property_verbatim_set',
'setter permission' => 'administer nodes',
'schema field' => 'created',
);
$properties['changed'] = array(
'label' => t("Date changed"),
'type' => 'date',
'schema field' => 'changed',
'description' => t("The date the node was most recently updated."),
);
$properties['author'] = array(
'label' => t("Author"),
'type' => 'user',
'description' => t("The author of the node."),
'setter callback' => 'entity_property_verbatim_set',
'setter permission' => 'administer nodes',
'required' => TRUE,
'schema field' => 'uid',
);
…
除了这些实体系统以外,字段系统也都被包含了进来,不过字段系统的代码比较抽象:
/**
* Implements hook_entity_property_info() on top of field module.
*
* @see entity_field_info_alter()
* @see entity_entity_property_info()
*/
function entity_metadata_field_entity_property_info() {
$info = array();
// Loop over all field instances and add them as property.
foreach (field_info_fields() as $field_name => $field) {
$field += array('bundles' => array());
if ($field_type = field_info_field_types($field['type'])) {
// Add in our default callback as the first one.
$field_type += array('property_callbacks' => array());
array_unshift($field_type['property_callbacks'], 'entity_metadata_field_default_property_callback');
foreach ($field['bundles'] as $entity_type => $bundles) {
foreach ($bundles as $bundle) {
$instance = field_info_instance($entity_type, $field_name, $bundle);
if ($instance && empty($instance['deleted'])) {
foreach ($field_type['property_callbacks'] as $callback) {
$callback($info, $entity_type, $field, $instance, $field_type);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return $info;
}
/**
* Callback to add in property info defaults per field instance.
* @see entity_metadata_field_entity_property_info().
*/
function entity_metadata_field_default_property_callback(&$info, $entity_type, $field, $instance, $field_type) {
if (!empty($field_type['property_type'])) {
if ($field['cardinality'] != 1) {
$field_type['property_type'] = 'list<' . $field_type['property_type'] . '>';
}
// Add in instance specific property info, if given and apply defaults.
$name = $field['field_name'];
$property = &$info[$entity_type]['bundles'][$instance['bundle']]['properties'][$name];
$instance += array('property info' => array());
$property = $instance['property info'] + array(
'label' => $instance['label'],
'type' => $field_type['property_type'],
'description' => t('Field "@name".', array('@name' => $name)),
'getter callback' => 'entity_metadata_field_property_get',
'setter callback' => 'entity_metadata_field_property_set',
'access callback' => 'entity_metadata_field_access_callback',
'query callback' => 'entity_metadata_field_query',
'translatable' => !empty($field['translatable']),
// Specify that this property stems from a field.
'field' => TRUE,
'required' => !empty($instance['required']),
);
// For field types of the list module add in the options list callback.
if (strpos($field['type'], 'list') === 0) {
$property['options list'] = 'entity_metadata_field_options_list';
}
}
}
Drupal核心系统,默认是不支持这个钩子的,但是Entity API模块把核心系统里面的所有涉及到的部分,都实现出来了。这里是包括所有的Drupal核心的字段类型的。我们在这里,前期不需要完全明白这些代码的含义,大致看一下,知道有这么回事就可以了,我们只需要记住,这里面,在属性数组信息里面,包含哪些常用的键就可以了。'label'、'description'、'getter callback'、'setter callback'、'sanitize'、'required'、'access callback'、'schema field'。有兴趣的话,可以沿着我们提示,把sites\all\modules\entity\modules下面,所有inc文件里面的代码都阅读一遍。注意,verbatim的中文意思为“完全)照字面的(地),逐字的(地)”,里面的代码会遇到这个单词。
Drupal版本:
6.2 entity_metadata_wrapper
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
Entity API模块,还提供了一个元数据封装器函数,entity_metadata_wrapper,通过这个函数的封装,我们可以更加方便的访问实体及其属性。这个函数给我们带来了哪些便利呢?我们通过代码示例来了解一下。
比如,获取节点作者的电子邮件地址,可以使用下面的代码:
$wrapper = entity_metadata_wrapper('node', $node);
$wrapper->author->mail->value();
我们在这里看到,封装过后的这个对象,在它上面,可以采用链式调用,此外它能够直接的建立关联关系。对于上面的功能,如果不使用封装器的话,我们通常采用这样的代码:
$uid = $node->uid;
$user = user_load($uid);
$mail = $user->mail;
这里,我们的代码也并不复杂,看不出来entity_metadata_wrapper的优越性。据文档里面说,$wrapper->author->mail->value();这段代码,可以省去user_load这个操作,直接通过关联关系获取到用户的电子邮件地址,这样可能会有一点小的性能提升。但是这也是有代价的,代价就是调用了entity_metadata_wrapper。通过这个例子,我们可以看到这个函数的基本用法。我们在前面让大家阅读代码的原因,就是为这里做准备的,为什么用的是$wrapper->author?而没有用$wrapper->uid,也没有用$wrapper->user?因为在hook_entity_property_info里面定义的是author。
为了更新用户的电子邮件地址,我们可以使用下面的代码:
$wrapper->author->mail->set('test@test.com');
或者
$wrapper->author->mail = 'test@test.com';
换成我们熟悉的代码,则是:
$user->mail = 'test@test.com';
user_save($user);
为了获取电子邮件的属性信息,可以使用下面的代码:
$mail_info = $wrapper->author->mail->info();
获取过滤了的节点标题:
$wrapper->title->value(array('sanitize' => TRUE));
获取原始数据:
$wrapper->body->value->raw();
上面的这几个例子都比较简单,我们看一个复杂的:
$wrapper->author->profile->field_name->value();
$wrapper->author->profile->field_name->set('新名字');
在这里,从节点,到节点的作者,再到作者的profile,再到profile上面的字段field_name,上面的一句,用来获取field_name字段的值,下面一句用来为该字段设置一个新值。如果我们自己写代码的话,需要加载用户对象,需要加载profile2对象,访问一个字段的值时,需要知道使用哪个语言来访问,代码写起来就比较复杂了。但是,在这里,一行代码就搞定了,非常方便。最后,我们再多看几个示例用法:
$wrapper->language('de')->body->summary->value();
$wrapper->author->mail->access('edit') ? TRUE : FALSE;
$wrapper->author->roles->optionsList();
$wrapper->field_files[0]->description = 'The first file';
$wrapper->save();
$node = $wrapper->value();
Drupal版本:
6.3 简化了实体类型的定义
作者:老葛,北京亚艾元软件有限责任公司,http://www.yaiyuan.com
这个模块还提供了一个Entity对象,如果我们要定义一个新的实体类型时,只需要继承这个对象就可以了,这个对象帮助我们实现了完整的CRUD操作。
在Entity API里面,所有的bundle,这里说的是Bundle本身,也都被处理成为了实体,这是一种可以导入、导出的实体。在Drupal核心中,内容类型的添加、编辑,是没有采用实体的形式的。Entity API模块,在这里走的更远,Bundle本身也处理成为了实体。我们看Profile2模块,在profile2_entity_info里面,可以找到这段代码:
$return['profile2_type'] = array(
'label' => t('Profile type'),
'plural label' => t('Profile types'),
'description' => t('Profiles types of Profile2 user profiles.'),
'entity class' => 'ProfileType',
'controller class' => 'EntityAPIControllerExportable',
'base table' => 'profile_type',
'fieldable' => FALSE,
'bundle of' => 'profile2',
'exportable' => TRUE,
'entity keys' => array(
'id' => 'id',
'name' => 'type',
'label' => 'label',
),
'access callback' => 'profile2_type_access',
'module' => 'profile2',
// Enable the entity API's admin UI.
'admin ui' => array(
'path' => 'admin/structure/profiles',
'file' => 'profile2.admin.inc',
'controller class' => 'Profile2TypeUIController',
),
);
通过这段代码,把Profile类型也处理成为实体了。对于这种包括Bundle类型的实体,Entity API还提供了一个管理界面,我们只需要对这个默认的管理界面进行扩展,就可以了。这里使用EntityDefaultUIController来管理默认的界面,Profile2TypeUIController则继承了EntityDefaultUIController。
如果我们基于Entity API来定义实体类型的话,此时与Views、Rules的集成都比较友好。Entity API模块提供了Views的基本集成,而Rules模块则是Fago的另一个杰作,本身就是基于Entity API模块的。